9VAC5-40-8140. Test methods and procedures.
A. The provisions governing test methods and procedures shall be as follows:
1. With regard to the emissions standards in 9VAC5-40-8080 and 9VAC5-40-8090, the provisions of 9VAC5-40-30 (Emission testing) apply.
2. With regard to the emission limits in 9VAC5-40-7970 through 9VAC5-40-8070, the following provisions apply:
a. 9VAC5-40-30 D and G.
b. 40 CFR 60.8, with the exception of paragraph (a).
c. 40 CFR 60.11 and 40 CFR 60.13.
d. Subsections B through J of this section.
B. The procedures and test methods specified in this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with the emission limits for particulate matter and opacity under 9VAC5-40-7970 and 9VAC5-40-8060.
1. Reference Method 1 shall be used to select sampling site and number of traverse points.
2. Reference Method 3, 3A, or 3B, as applicable, shall be used for gas analysis.
3. Reference Method 5 shall be used for determining compliance with the particulate matter emission limit. The minimum sample volume shall be 1.7 cubic meters. The probe and filter holder heating systems in the sample train shall be set to provide a gas temperature no greater than 160 ± 14 degrees Centigrade. An oxygen or carbon dioxide measurement shall be obtained simultaneously with each Reference Method 5 run.
4. The owner of an affected facility may request that compliance with the particulate matter emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 B 6.
5. As specified in 40 CFR 60.8, all emission tests shall consist of three test runs. The average of the particulate matter emission concentrations from the three test runs is used to determine compliance.
6. In accordance with subdivisions 7 and 10 of this subsection, Reference Method 9 shall be used for determining compliance with the opacity limit except as provided in 40 CFR 60.11(e).
7. The owner of an affected facility shall conduct an initial emission test for particulate matter emissions and opacity as required in 9VAC5-40-8100.
8. The owner of an affected facility shall install, calibrate, maintain, and operate a continuous opacity monitoring system for measuring opacity and shall follow the methods and procedures specified in subdivisions 8 a through 8 d of this subsection.
a. The output of the continuous opacity monitoring system shall be recorded on a 6-minute average basis.
b. The continuous opacity monitoring system shall be installed, evaluated, and operated in accordance with 40 CFR 60.13.
c. The continuous opacity monitoring system shall conform to Performance Specification 1 in Appendix B of 40 CFR Part 60.
d. The initial performance evaluation shall be completed as specified in 9VAC5-40-8100.
9. Following the date that the initial emission test for particulate matter is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100 for an affected facility, the owner shall conduct an emission test for particulate matter on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months following the previous emission test).
10. Following the date that the initial emission test for opacity is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100 for an affected facility, the owner shall conduct an emission test for opacity on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months following the previous emission test) using the test method specified in subdivision 6 of this subsection.
C. The procedures and test methods specified in this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with the emission limits for cadmium, lead, and mercury under 9VAC5-40-7990, 9VAC5-40-8000, and 9VAC5-40-8010.
1. The procedures and test methods specified in subdivisions 1 a through 1 g of this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with the emission limits for cadmium and lead under 9VAC5-40-7990 and 9VAC5-40-8000.
a. Reference Method 1 shall be used for determining the location and number of sampling points.
b. Reference Method 3, 3A, or 3B, as applicable, shall be used for flue gas analysis.
c. Reference Method 29 shall be used for determining compliance with the cadmium and lead emission limits.
d. An oxygen or carbon dioxide measurement shall be obtained simultaneously with each Reference Method 29 test run for cadmium and lead required under subdivision 1 c of this subsection.
e. The owner of an affected facility may request that compliance with the cadmium or lead emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 B 6.
f. All emission tests shall consist of a minimum of three test runs conducted under representative full load operating conditions. The average of the cadmium or lead emission concentrations from three test runs or more shall be used to determine compliance.
g. Following the date of the initial emission test or the date on which the initial emission test is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100, the owner of an affected facility shall conduct an emission test for compliance with the emission limits for cadmium and lead on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months following the previous emission test).
2. The procedures and test methods specified in subdivisions 2 a through 2 j of this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with the mercury emission limit under 9VAC5-40-8010.
a. Reference Method 1 shall be used for determining the location and number of sampling points.
b. Reference Method 3, 3A, or 3B, as applicable, shall be used for flue gas analysis.
c. Reference Method 29 shall be used to determine the mercury emission concentration. The minimum sample volume when using Reference Method 29 for mercury shall be 1.7 cubic meters.
d. An oxygen (or carbon dioxide) measurement shall be obtained simultaneously with each Reference Method 29 test run for mercury required under subdivision 2 c of this subsection.
e. The percent reduction in the potential mercury emissions (% pHg) is computed using the following equation:
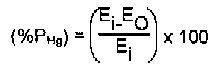
where:
%PHg = percent reduction of the potential mercury emissions achieved.
Ei = potential mercury emission concentration measured at the control device inlet, corrected to 7.0% oxygen (dry basis).
EO = controlled mercury emission concentration measured at the mercury control device outlet, corrected to 7.0% oxygen (dry basis).
f. All emission tests shall consist of a minimum of three test runs conducted under representative full load operating conditions. The average of the mercury emission concentrations or percent reductions from three test runs or more is used to determine compliance.
g. The owner of an affected facility may request that compliance with the mercury emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 B 6.
h. The owner of an affected facility shall conduct an initial emission test for mercury emissions as required in 9VAC5-40-8100.
i. Following the date that the initial emission test for mercury is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100, the owner of an affected facility shall conduct an emission test for mercury emissions on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months from the previous emission test).
j. The owner of an affected facility where activated carbon injection is used to comply with the mercury emission limit shall follow the procedures specified in subsection J of this section for measuring and calculating carbon usage.
D. The procedures and test methods specified in this subsection shall be used for determining compliance with the sulfur dioxide emission limit under 9VAC5-40-8020.
1. Reference Method 19, section 4.3, shall be used to calculate the daily geometric average sulfur dioxide emission concentration.
2. Reference Method 19, section 5.4, shall be used to determine the daily geometric average percent reduction in the potential sulfur dioxide emission concentration.
3. The owner of an affected facility may request that compliance with the sulfur dioxide emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 B 6.
4. The owner of an affected facility shall conduct an initial emission test for sulfur dioxide emissions as required in 9VAC5-40-8100. Compliance with the sulfur dioxide emission limit (concentration or percent reduction) shall be determined by using the continuous emission monitoring system specified in subdivision 5 of this subsection to measure sulfur dioxide and calculating a 24-hour daily geometric average emission concentration or a 24-hour daily geometric average percent reduction using Reference Method 19, sections 4.3 and 5.4, as applicable.
5. The owner of an affected facility shall install, calibrate, maintain, and operate a continuous emission monitoring system for measuring sulfur dioxide emissions discharged to the atmosphere and record the output of the system.
6. Following the date that the initial emission test for sulfur dioxide is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100, compliance with the sulfur dioxide emission limit shall be determined based on the 24-hour daily geometric average of the hourly arithmetic average emission concentrations using continuous emission monitoring system outlet data if compliance is based on an emission concentration, or continuous emission monitoring system inlet and outlet data if compliance is based on a percent reduction.
7. At a minimum, valid continuous monitoring system hourly averages shall be obtained as specified in subdivisions 7 a and 7 b of this subsection for 75% of the operating hours per day for 90% of the operating days per calendar quarter that the affected facility is combusting municipal solid waste.
a. At least two data points per hour shall be used to calculate each one-hour arithmetic average.
b. Each sulfur dioxide one-hour arithmetic average shall be corrected to 7.0% oxygen on an hourly basis using the one-hour arithmetic average of the oxygen (or carbon dioxide) continuous emission monitoring system data.
8. The one-hour arithmetic averages required under subdivision 6 of this subsection shall be expressed in parts per million corrected to 7.0% oxygen (dry basis) and used to calculate the 24-hour daily geometric average emission concentrations and daily geometric average emission percent reductions. The one-hour arithmetic averages shall be calculated using the data points required in 40 CFR 60.13(e)(2).
9. All valid continuous emission monitoring system data shall be used in calculating average emission concentrations and percent reductions even if the minimum continuous emission monitoring system data requirements of subdivision 7 of this subsection are not met.
10. The procedures in 40 CFR 60.13 shall be followed for installation, evaluation, and operation of the continuous emission monitoring system.
11. The initial performance evaluation shall be completed as specified in 9VAC5-40-8100.
12. The continuous emission monitoring system shall be operated according to Performance Specification 2 in Appendix B of 40 CFR Part 60.
a. During each relative accuracy test run of the continuous emission monitoring system required by Performance Specification 2 in Appendix B of 40 CFR Part 60, sulfur dioxide and oxygen (or carbon dioxide) data shall be collected concurrently (or within a 30- to 60-minute period) by both the continuous emission monitors and the test methods specified in subdivisions 12 a (1) and 12 a (2) of this subsection.
(1) For sulfur dioxide, Reference Method 6, 6A, or 6C shall be used.
(2) For oxygen (or carbon dioxide), Reference Method 3, 3A, or 3B, as applicable, shall be used.
b. The span value of the continuous emissions monitoring system at the inlet to the sulfur dioxide control device shall be 125% of the maximum estimated hourly potential sulfur dioxide emissions of the municipal waste combustor unit. The span value of the continuous emission monitoring system at the outlet of the sulfur dioxide control device shall be 50% of the maximum estimated hourly potential sulfur dioxide emissions of the municipal waste combustor unit.
13. Quarterly accuracy determinations and daily calibration drift tests shall be performed in accordance with procedure 1 in Appendix F of 40 CFR Part 60.
14. When sulfur dioxide emissions data are not obtained because of continuous emission monitoring system breakdowns, repairs, calibration checks, and zero and span adjustments, emissions data shall be obtained by using other monitoring systems as approved by the board or Reference Method 19 to provide, as necessary, valid emissions data for a minimum of 75% of the hours per day that the affected facility is operated and combusting municipal solid waste for 90% of the days per calendar quarter that the affected facility is operated and combusting municipal solid waste.
E. The procedures and test methods specified in this subsection shall be used for determining compliance with the hydrogen chloride emission limit under 9VAC5-40-8030.
1. Reference Method 26 or 26A, as applicable, shall be used to determine the hydrogen chloride emission concentration. The minimum sampling time for Reference Method 26 shall be one hour.
2. An oxygen (or carbon dioxide) measurement shall be obtained simultaneously with each Reference Method 26 test run for hydrogen chloride required by subdivision 1 of this subsection.
3. The percent reduction in potential hydrogen chloride emissions (%PHCl) is computed using the following equation:

where:
%PHCl = percent reduction of the potential hydrogen chloride emissions achieved.
Ei = potential hydrogen chloride emission concentration measured at the control device inlet, corrected to 7.0% oxygen (dry basis).
EO = controlled hydrogen chloride emission concentration measured at the control device outlet, corrected to 7.0% oxygen (dry basis).
4. The owner of an affected facility may request that compliance with the hydrogen chloride emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 B 6.
5. As specified in 40 CFR 60.8, all emission tests shall consist of three test runs. The average of the hydrogen chloride emission concentrations or percent reductions from the three test runs is used to determine compliance.
6. The owner of an affected facility shall conduct an initial emission test for hydrogen chloride as required in 9VAC5-40-8100.
7. Following the date that the initial emission test for hydrogen chloride is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100, the owner of an affected facility shall conduct an emission test for hydrogen chloride emissions on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months following the previous emission test).
F. The procedures and test methods specified in this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with the limits for dioxin/furan emissions under 9VAC5-40-8040.
1. Reference Method 1 shall be used for determining the location and number of sampling points.
2. Reference Method 3, 3A, or 3B, as applicable, shall be used for flue gas analysis.
3. Reference Method 23 shall be used for determining the dioxin/furan emission concentration.
a. The minimum sample time shall be four hours per test run.
b. An oxygen (or carbon dioxide) measurement shall be obtained simultaneously with each Reference Method 23 test run for dioxins/furans.
4. The owner of an affected facility shall conduct an initial emission test for dioxin/furan emissions in accordance with subdivision 3 of this subsection, as required in 9VAC5-40-8100.
5. Following the date that the initial emission test for dioxins/furans is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100, the owner of an affected facility shall conduct emission tests for dioxin/furan emissions in accordance with subdivision 3 of this subsection, according to one of the schedules specified in subdivision 5 a or 5 b of this subsection.
a. For affected facilities, emission tests shall be conducted on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months following the previous emission test).
b. Where all emission tests over a two-year period indicate that dioxin/furan emissions are less than or equal to 15 nanograms per dry standard cubic meter (total mass) for all affected facilities located within a municipal waste combustor plant, the owner of the municipal waste combustor plant may elect to conduct annual emission tests for one affected facility (i.e., unit) per year at the municipal waste combustor plant. At a minimum, an emission test for dioxin/furan emissions shall be conducted annually (no more than 12 months following the previous emission test) for one affected facility at the municipal waste combustor plant. Each year a different affected facility at the municipal waste combustor plant shall be tested, and the affected facilities at the plant shall be tested in sequence (e.g., unit 1, unit 2, unit 3, as applicable). If each annual emission test continues to indicate a dioxin/furan emission level less than or equal to 15 nanograms per dry standard cubic meter (total mass), the owner may continue conducting an emission test on only one affected facility per year. If any annual emission test indicates a dioxin/furan emission level greater than 15 nanograms per dry standard cubic meter (total mass), emission tests thereafter shall be conducted annually on all affected facilities at the plant until and unless all annual emission tests for all affected facilities at the plant over a two-year period indicate a dioxin/furan emission level less than or equal to 15 nanograms per dry standard cubic meter (total mass).
6. The owner of an affected facility that selects to follow the emission testing schedule specified in subdivision 5 a or 5 b of this subsection shall follow the procedures specified in 9VAC5-40-8160 D 4 for reporting the selection of this schedule.
7. The owner of an affected facility where activated carbon is used to comply with the dioxin/furan emission limits specified in 9VAC5-40-8040 or the dioxin/furan emission level specified in subdivision 5 a or 5 b of this subsection shall follow the procedures specified in subsection J of this section for measuring and calculating the carbon usage rate.
8. The owner may request that compliance with the dioxin/furan emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 B 6.
9. As specified in 40 CFR 60.8, all emission tests shall consist of three test runs. The average of the dioxin/furan emission concentrations from the three test runs is used to determine compliance.
G. The procedures and test methods specified in this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with the nitrogen oxides emission limit for affected facilities under 9VAC5-40-8050.
1. Reference Method 19, section 4.1, shall be used for determining the daily arithmetic average nitrogen oxides emission concentration.
2. The owner of an affected facility may request that compliance with the nitrogen oxides emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 B 6.
3. The owner of an affected facility subject to the nitrogen oxides limit under 9VAC5-40-8050 shall conduct an initial emission test for nitrogen oxides as required in 9VAC5-40-8100. Compliance with the nitrogen oxides emission limit shall be determined by using the continuous emission monitoring system specified in subdivision 4 of this subsection for measuring nitrogen oxides and calculating a 24-hour daily arithmetic average emission concentration using Reference Method 19, section 4.1.
4. The owner of an affected facility subject to the nitrogen oxides emission limit under 9VAC5-40-8050 shall install, calibrate, maintain, and operate a continuous emission monitoring system for measuring nitrogen oxides discharged to the atmosphere, and record the output of the system.
5. Following the date that the initial emission test for nitrogen oxides is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100, compliance with the emission limit for nitrogen oxides required under 9VAC5-40-8050 shall be determined based on the 24-hour daily arithmetic average of the hourly emission concentrations using continuous emission monitoring system outlet data.
6. At a minimum, valid continuous emission monitoring system hourly averages shall be obtained as specified in subdivisions 6 a and 6 b of this subsection for 75% of the operating hours per day for 90% of the operating days per calendar quarter that the affected facility is combusting municipal solid waste.
a. At least two data points per hour shall be used to calculate each one-hour arithmetic average.
b. Each nitrogen oxides one-hour arithmetic average shall be corrected to 7.0% oxygen on an hourly basis using the one-hour arithmetic average of the oxygen (or carbon dioxide) continuous emission monitoring system data.
7. The one-hour arithmetic averages required by subdivision 5 of this subsection shall be expressed in parts per million by volume (dry basis) and used to calculate the 24-hour daily arithmetic average concentrations. The one-hour arithmetic averages shall be calculated using the data points required in 40 CFR 60.13(e)(2).
8. All valid continuous emission monitoring system data must be used in calculating emission averages even if the minimum continuous emission monitoring system data requirements of subdivision 6 of this subsection are not met.
9. The procedures in 40 CFR 60.13 shall be followed for installation, evaluation, and operation of the continuous emission monitoring system. The initial performance evaluation shall be completed as specified in 9VAC5-40-8100.
10. The owner of an affected facility shall operate the continuous emission monitoring system according to Performance Specification 2 in Appendix B of 40 CFR Part 60 and shall follow the procedures and methods specified in subdivisions 10 a and 10 b of this subsection.
a. During each relative accuracy test run of the continuous emission monitoring system required by Performance Specification 2 of Appendix B of 40 CFR Part 60, nitrogen oxides and oxygen (or carbon dioxide) data shall be collected concurrently (or within a 30- to 60-minute period) by both the continuous emission monitors and the test methods specified in subdivisions 10 a (1) and 10 a (2) of this subsection.
(1) For nitrogen oxides, Reference Method 7, 7A, 7C, 7D, or 7E shall be used.
(2) For oxygen (or carbon dioxide), Reference Method 3, 3A, or 3B, as applicable, shall be used.
b. The span value of the continuous emission monitoring system shall be 125% of the maximum estimated hourly potential nitrogen oxide emissions of the municipal waste combustor unit.
11. Quarterly accuracy determinations and daily calibration drift tests shall be performed in accordance with procedure 1 in Appendix F of 40 CFR Part 60.
12. When nitrogen oxides continuous emissions data are not obtained because of continuous emission monitoring system breakdowns, repairs, calibration checks, and zero and span adjustments, emissions data shall be obtained using other monitoring systems as approved by the board or Reference Method 19 to provide, as necessary, valid emissions data for a minimum of 75% of the hours per day for 90% of the days per calendar quarter the unit is operated and combusting municipal solid waste.
H. The procedures specified in this subsection shall be used for determining compliance with the fugitive ash emission limit under 9VAC5-40-8070.
1. Reference Method 22 shall be used for determining compliance with the fugitive ash emission limit under 9VAC5-40-8070. The minimum observation time shall be a series of three one-hour observations. The observation period shall include times when the facility is transferring ash from the municipal waste combustor unit to the area where ash is stored or loaded into containers or trucks.
2. The average duration of visible emissions per hour shall be calculated from the three one-hour observations. The average shall be used to determine compliance with 9VAC5-40-8070.
3. The owner of an affected facility shall conduct an initial emission test for fugitive ash emissions as required in 9VAC5-40-8100.
4. Following the date that the initial emission test for fugitive ash emissions is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100 for an affected facility, the owner shall conduct an emission test for fugitive ash emissions on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months following the previous emission test).
I. The procedures specified in this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with the opacity limit for air curtain incinerators under 9VAC5-40-8060 C.
1. Reference Method 9 shall be used for determining compliance with the opacity limit.
2. The owner of the air curtain incinerator shall conduct an initial emission test for opacity as required in 9VAC5-40-8100.
3. Following the date that the initial emission test is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100, the owner of the air curtain incinerator shall conduct an emission test for opacity on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months following the previous emission test).
J. The owner of an affected facility where activated carbon injection is used to comply with the mercury emission limit under 9VAC5-40-8010, or the dioxin/furan emission limits under 9VAC5-40-8040, or the dioxin/furan emission level specified in subdivision F 5 b of this section shall follow the procedures specified in this subsection.
1. During the emission tests for dioxins/furans and mercury, as applicable, the owner shall estimate an average carbon mass feed rate based on carbon injection system operating parameters such as the screw feeder speed, hopper volume, hopper refill frequency, or other parameters appropriate to the feed system being employed, as specified in subdivisions 1 a and 1 b of this subsection.
a. An average carbon mass feed rate in kilograms per hour or pounds per hour shall be estimated during the initial emission test for mercury emissions and each subsequent emission test for mercury emissions.
b. An average carbon mass feed rate in kilograms per hour or pounds per hour shall be estimated during the initial emission test for dioxin/furan emissions and each subsequent emission test for dioxin/furan emissions.
2. During operation of the affected facility, the carbon injection system operating parameter(s) that are the primary indicator(s) of the carbon mass feed rate (e.g., screw feeder setting) must equal or exceed the level(s) documented during the emission tests specified under subdivisions 1 a and 1 b of this subsection.
3. The owner of an affected facility shall estimate the total carbon usage of the plant (kilograms or pounds) for each calendar quarter by two independent methods, according to the procedures in subdivisions 3 a and 3 b of this subsection.
a. The weight of carbon delivered to the plant.
b. Estimate the average carbon mass feed rate in kilograms per hour or pounds per hour for each hour of operation for each affected facility based on the parameters specified under subdivision 1 of this subsection, and sum the results for all affected facilities at the plant for the total number of hours of operation during the calendar quarter.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999; amended, Virginia Register Volume 19, Issue 17, eff. July 1, 2003.