Article 54. Emission Standards for Large Municipal Waste Combustors (Rule 4-54)
9VAC5-40-7950. Applicability and designation of affected facility.
Article 54
Emission Standards for Large Municipal Waste Combustors (Rule 4-54)
A. Except as provided in subsections D and E of this section, the affected facility to which the provisions of this article apply is each municipal waste combustor unit with a combustion capacity greater than 250 tons per day of municipal solid waste for which construction was commenced on or before September 20, 1994.
B. The provisions of this article apply throughout the Commonwealth of Virginia.
C. Air curtain incinerators that meet the capacity specifications in subsection A of this section and that combust municipal solid waste other than yard waste are subject to all provisions of this article.
D. Exempted from the provisions of this article are the following:
1. Any waste combustion unit that is capable of combusting more than 250 tons per day of municipal solid waste and is subject to a federally enforceable permit limiting the maximum amount of municipal solid waste that may be combusted in the unit to less than or equal to 11 tons per day is not subject to this article if the owner:
a. Notifies the board of an exemption claim;
b. Provides a copy of the federally enforceable permit that limits the firing of municipal solid waste to less than 11 tons per day; and
c. Keeps records of the amount of municipal solid waste fired on a daily basis.
2. Physical or operational changes made to an existing municipal waste combustor unit primarily for the purpose of complying with this article are not considered in determining whether the unit is a modified or reconstructed facility under subpart Ea or subpart Eb of 40 CFR Part 60.
3. A qualifying small power production facility, as defined in § 3(17)(C) of the Federal Power Act (16 USC § 796(17)(C)), that burns homogeneous waste (such as automotive tires or used oil, but not including refuse-derived fuel) for the production of electric energy is not subject to this article if the owner of the facility notifies the board of this exemption and provides data documenting that the facility qualifies for this exemption.
4. A qualifying cogeneration facility, as defined in § 3(18)(B) of the Federal Power Act (16 §USC 796(18)(B)), that burns homogeneous waste (such as automotive tires or used oil, but not including refuse-derived fuel) for the production of electric energy and steam or forms of useful energy (such as heat) that are used for industrial, commercial, heating, or cooling purposes, is not subject to this article if the owner of the facility notifies the board of this exemption and provides data documenting that the facility qualifies for this exemption.
5. Any unit combusting a single-item waste stream of tires is not subject to this article if the owner of the unit notifies the board of an exemption claim, and provides data documenting that the unit qualifies for this exemption.
6. Any cofired combustor located at a plant that meets the capacity specifications in subsection A of this section is not subject to this article if the owner of the cofired combustor:
a. Notifies the board of an exemption claim;
b. Provides a copy of the federally enforceable permit (specified in the definition of cofired combustor in 9VAC5-40-7960); and
c. Keeps a record on a calendar quarter basis of the weight of municipal solid waste combusted at the cofired combustor and the weight of all other fuels combusted at the cofired combustor.
7. Air curtain incinerators that meet the capacity specifications in subsection A of this section and that combust a fuel stream composed of 100% yard waste are exempt from all provisions of this article except the opacity limit under 9VAC5-40-8060 C, the testing procedures under 9VAC5-40-8140, and the reporting and recordkeeping provisions under 9VAC5-40-8160.
8. Pyrolysis/combustion units that are an integrated part of a plastics/rubber recycling unit are not subject to this article if the owner of the plastics/rubber recycling unit keeps records of:
a. The weight of plastics, rubber, and rubber tires, or a combination thereof, processed on a calendar quarter basis;
b. The weight of chemical plant feedstocks and petroleum refinery feedstocks produced and marketed on a calendar quarter basis; and
c. The name and address of the purchaser of the feedstocks. The combustion of gasoline, diesel fuel, jet fuel, fuel oils, residual oil, refinery gas, petroleum coke, liquefied petroleum gas, propane, or butane produced by chemical plants or petroleum refineries that use feedstocks produced by plastics/rubber recycling units are not subject to this article.
E. The provisions of this article do not apply to the following:
1. Any unit required to have a permit under § 3005 of the Solid Waste Disposal Act (42 USC § 6901 et seq.).
2. Any materials recovery facility (including primary or secondary smelters) that combusts waste for the primary purpose of recovering metals.
3. Any cement kiln firing municipal solid waste.
F. The provisions of 40 CFR Part 60 cited in this article are applicable only to the extent that they are incorporated by reference in Article 5 (9VAC5-50-400 et seq.) of Part II of 9VAC5 Chapter 50.
G. The requirement of subdivision E 1 of this section with regard to obtaining a permit under § 3005 of the Solid Waste Disposal Act (42 USC § 6901 et seq.) may be met by obtaining a permit from the department as required by 9VAC20 Chapter 60.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999; amended, Virginia Register Volume 19, Issue 17, eff. July 1, 2003.
9VAC5-40-7960. Definitions.
A. For the purpose of applying this article in the context of the Regulations for the Control and Abatement of Air Pollution and related uses, the words or terms shall have the meanings given them in subsection C of this section.
B. As used in this article, all terms not defined herein shall have the meanings given them in 9VAC5 Chapter 10, unless otherwise required by context.
C. Terms defined.
"Air curtain incinerator" means an incinerator that operates by forcefully projecting a curtain of air across an open chamber or pit in which burning occurs. Incinerators of this type can be constructed above or below ground and with or without refractory walls and floor.
"Batch municipal waste combustor" means a municipal waste combustor unit designed so that it cannot combust municipal solid waste continuously 24 hours per day because the design does not allow waste to be fed to the unit or ash to be removed while combustion is occurring.
"Bubbling fluidized bed combustor" means a fluidized bed combustor in which the majority of the bed material remains in a fluidized state in the primary combustion zone.
"Calendar quarter" means a consecutive three-month period (nonoverlapping) beginning on January 1, April 1, July 1, and October 1.
"Calendar year" means the period including 365 days (or 336 consecutive days in leap years) starting January 1 and ending on December 31.
"Chief facility operator" means the person in direct charge and control of the operation of a municipal waste combustor and who is responsible for daily onsite supervision, technical direction, management, and overall performance of the facility.
"Circulating fluidized bed combustor" means a fluidized bed combustor in which the majority of the fluidized bed material is carried out of the primary combustion zone and is transported back to the primary zone through a recirculation loop.
"Clean wood" means untreated wood or untreated wood products including clean untreated lumber, tree stumps (whole or chipped), and tree limbs (whole or chipped). Clean wood does not include yard waste, which is defined elsewhere in this section, or construction, renovation, and demolition wastes (including but not limited to railroad ties and telephone poles), which are exempt from the definition of municipal solid waste in this section.
"Cofired combustor" means a unit combusting municipal solid waste with nonmunicipal solid waste fuel (e.g., coal, industrial process waste) and subject to a federally enforceable permit limiting the unit to combusting a fuel feed stream, 30% or less of the weight of which is comprised, in aggregate, of municipal solid waste as measured on a calendar quarter basis.
"Commenced" means that an owner has undertaken a continuous program of construction or modification or that an owner has entered into a contractual obligation to undertake and complete, within a reasonable time, a continuous program of construction or modification.
"Compliance schedule" means a legally enforceable schedule specifying a date or dates by which a source or category of sources must comply with specific emission standards contained in a plan or with any increments of progress to achieve such compliance.
"Construction" means fabrication, erection, or installation of an affected facility.
"Continuous emission monitoring system" means a monitoring system for continuously measuring the emissions of a pollutant from an affected facility.
"Dioxin/furan" means tetra- through octa- chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans.
"First calendar half" means the period starting on January 1 and ending on June 30 in any year.
"Four-hour block average" means the average of all hourly emission concentrations when the affected facility is operating and combusting municipal solid waste measured over four-hour periods of time from midnight to 4 a.m., 4 a.m. to 8 a.m., 8 a.m. to noon, noon to 4 p.m., 4 p.m. to 8 p.m., and 8 p.m. to midnight.
"Increments of process" means steps to achieve compliance which must be taken by an owner of an affected facility, including:
1. Submittal of a final control plan for the affected facility to the board;
2. Awarding of contracts for emission control systems or for process modifications or issuance of orders for the purchase of component parts to accomplish emission control or process modification;
3. Initiation of on-site construction or installation of emission control equipment or process change;
4. Completion of on-site construction or installation or emission control equipment or process change; and
5. Final compliance.
"Mass burn refractory municipal waste combustor" means a field-erected combustor that combusts municipal solid waste in a refractory wall furnace. Unless otherwise specified, this includes combustors with a cylindrical rotary refractory wall furnace.
"Mass burn rotary waterwall municipal waste combustor" means a field-erected combustor that combusts municipal solid waste in a cylindrical rotary waterwall furnace or on a tumbling-tile grate.
"Mass burn waterwall municipal waste combustor" means a field-erected combustor that combusts municipal solid waste in a waterwall furnace.
"Materials separation plan" means a plan that identifies both a goal and an approach to separate certain components of municipal solid waste for a given service area in order to make the separated materials available for recycling. A materials separation plan may include elements such as dropoff facilities, buy-back or deposit-return incentives, curbside pickup programs, or centralized mechanical separation systems. A materials separation plan may include different goals or approaches for different subareas in the service area, and may include no materials separation activities for certain subareas or, if warranted, an entire service area.
"Maximum demonstrated municipal waste combustor unit load" means the highest four-hour arithmetic average municipal waste combustor unit load achieved during four consecutive hours during the most recent dioxin/furan emission test demonstrating compliance with the applicable limit for municipal waste combustor organics specified under 9VAC5-40-8040.
"Maximum demonstrated particulate matter control device temperature" means the highest four-hour arithmetic average flue gas temperature measured at the particulate matter control device inlet during four consecutive hours during the most recent dioxin/furan emission test demonstrating compliance with the applicable limit for municipal waste combustor organics specified under 9VAC5-40-8040.
"Modification" or "modified municipal waste combustor unit" means a municipal waste combustor unit to which changes have been made after June 19, 1996, if (i) the cumulative cost of the changes, over the life of the unit, exceed 50% of the original cost of construction and installation of the unit (not including the cost of any land purchased in connection with such construction or installation) updated to current costs or (ii) any physical change in the municipal waste combustor unit or change in the method of operation of the municipal waste combustor unit increases the amount of any air pollutant emitted by the unit for which standards have been established under § 129 or § 111 of the federal Clean Air Act. Increases in the amount of any air pollutant emitted by the municipal waste combustor unit are determined at 100% physical load capability and downstream of all air pollution control devices, with no consideration given for load restrictions based on permits or other nonphysical operational restrictions.
"Modular excess-air municipal waste combustor" means a combustor that combusts municipal solid waste and that is not field-erected and has multiple combustion chambers, all of which are designed to operate at conditions with combustion air amounts in excess of theoretical air requirements.
"Modular starved-air municipal waste combustor" means a combustor that combusts municipal solid waste and that is not field-erected and has multiple combustion chambers in which the primary combustion chamber is designed to operate at substoichiometric conditions.
"Municipal solid waste" or "municipal-type solid waste" means household, commercial/retail, and institutional waste, or a combination thereof. Household waste includes material discarded by single and multiple residential dwellings, hotels, motels, and other similar permanent or temporary housing establishments or facilities. Commercial/retail waste includes material discarded by stores, offices, restaurants, warehouses, nonmanufacturing activities at industrial facilities, and other similar establishments or facilities. Institutional waste includes material discarded by schools, nonmedical waste discarded by hospitals, material discarded by nonmanufacturing activities at prisons and government facilities, and material discarded by other similar establishments or facilities. Household, commercial/retail, and institutional waste does not include used oil; sewage sludge; wood pallets; construction, renovation, and demolition wastes (which includes but is not limited to railroad ties and telephone poles); clean wood; industrial process or manufacturing wastes; medical waste; or motor vehicles (including motor vehicle parts or vehicle fluff). Household, commercial/retail, and institutional wastes include (i) yard waste, (ii) refuse-derived fuel, and (iii) motor vehicle maintenance materials limited to vehicle batteries and tires except as specified in 9VAC5-40-7950 D 5.
"Municipal waste combustor" or "municipal waste combustor unit" means any setting or equipment that combusts solid, liquid, or gasified municipal solid waste including, but not limited to, field-erected incinerators (with or without heat recovery), modular incinerators (starved-air or excess-air), boilers (i.e., steam generating units), furnaces (whether suspension-fired, grate-fired, mass-fired, air curtain incinerators, or fluidized bed-fired), and pyrolysis/combustion units. Municipal waste combustors do not include pyrolysis/combustion units located at a plastics/rubber recycling unit (as specified in 9VAC5-40-7950 D 8). Municipal waste combustors do not include cement kilns firing municipal solid waste (as specified in 9VAC5-40-7950 E 3). Municipal waste combustors do not include internal combustion engines, gas turbines, or other combustion devices that combust landfill gases collected by landfill gas collection systems.
The boundaries of a municipal solid waste combustor are defined as follows. The municipal waste combustor unit includes, but is not limited to, the municipal solid waste fuel feed system, grate system, flue gas system, bottom ash system, and the combustor water system. The municipal waste combustor boundary starts at the municipal solid waste pit or hopper and extends through:
1. The combustor flue gas system, which ends immediately following the heat recovery equipment or, if there is no heat recovery equipment, immediately following the combustion chamber;
2. The combustor bottom ash system, which ends at the truck loading station or similar ash handling equipment that transfer the ash to final disposal, including all ash handling systems that are connected to the bottom ash handling system; and
3. The combustor water system, which starts at the feed water pump and ends at the piping exiting the steam drum or superheater.
The municipal waste combustor unit does not include air pollution control equipment, the stack, water treatment equipment, or the turbine-generator set.
"Municipal waste combustor acid gases" means all acid gases emitted in the exhaust gases from municipal waste combustor units including, but not limited to, sulfur dioxide and hydrogen chloride gases.
"Municipal waste combustor metals" means metals and metal compounds emitted in the exhaust gases from municipal waste combustor units.
"Municipal waste combustor organics" means organic compounds emitted in the exhaust gases from municipal waste combustor units and includes tetra- through octa- chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans.
"Municipal waste combustor plant" means one or more affected facilities (as specified in 9VAC5-40-7950) at the same location.
"Municipal waste combustor unit capacity" means the maximum charging rate of a municipal waste combustor unit expressed in tons per day of municipal solid waste combusted, calculated according to the procedures under 9VAC5-40-8100 C. 9VAC5-40-8100 C includes procedures for determining municipal waste combustor unit capacity for continuous and batch feed municipal waste combustors.
"Municipal waste combustor unit load" means the steam load of the municipal waste combustor unit measured as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 C 6.
"Particulate matter" means total particulate matter emitted from municipal waste combustor units as measured by Reference Method 5 (see 9VAC5-40-8140 B).
"Plastics/rubber recycling unit" means an integrated processing unit where plastics, rubber, and rubber tires, or a combination thereof, are the only feed materials (incidental contaminants may be included in the feed materials) and they are processed into a chemical plant feedstock or petroleum refinery feedstock, where the feedstock is marketed to and used by a chemical plant or petroleum refinery as input feedstock. The combined weight of the chemical plant feedstock and petroleum refinery feedstock produced by the plastics/rubber recycling unit on a calendar quarter basis shall be more than 70% of the combined weight of the plastics, rubber, and rubber tires processed by the plastics/rubber recycling unit on a calendar quarter basis. The plastics, rubber, or rubber tire feed materials to the plastics/rubber recycling unit may originate from the separation or diversion of plastics, rubber, or rubber tires from MSW or industrial solid waste, and may include manufacturing scraps, trimmings, and off-specification plastics, rubber, and rubber tire discards. The plastics, rubber, and rubber tire feed materials to the plastics/rubber recycling unit may contain incidental contaminants (e.g., paper labels on plastic bottles, metal rings on plastic bottle caps, etc.).
"Potential hydrogen chloride emission concentration" means the hydrogen chloride emission concentration that would occur from combustion of municipal solid waste in the absence of any emission controls for municipal waste combustor acid gases.
"Potential mercury emission concentration" means the mercury emission concentration that would occur from combustion of municipal solid waste in the absence of any mercury emissions control.
"Potential sulfur dioxide emissions" means the sulfur dioxide emission concentration that would occur from combustion of municipal solid waste in the absence of any emission controls for municipal waste combustor acid gases.
"Pulverized coal/refuse-derived fuel mixed fuel-fired combustor" means a combustor that fires coal and refuse-derived fuel simultaneously, in which pulverized coal is introduced into an air stream that carries the coal to the combustion chamber of the unit where it is fired in suspension. This includes both conventional pulverized coal and micropulverized coal.
"Pyrolysis/combustion unit" means a unit that produces gases, liquids, or solids through the heating of municipal solid waste, and the gases, liquids, or solids produced are combusted and emissions vented to the atmosphere.
"Reconstruction" means rebuilding a municipal waste combustor unit for which the reconstruction commenced after June 19, 1996, and the cumulative costs of the construction over the life of the unit exceed 50% of the original cost of construction and installation of the unit (not including any cost of land purchased in connection with such construction or installation) updated to current costs (current dollars).
"Refractory unit" or "refractory wall furnace" means a combustion unit having no energy recovery (e.g., via a waterwall) in the furnace (i.e., radiant heat transfer section) of the combustor.
"Refuse-derived fuel" means a type of municipal solid waste produced by processing municipal solid waste through shredding and size classification. This includes all classes of refuse-derived fuel including low-density fluff refuse-derived fuel through densified refuse-derived fuel and pelletized refuse-derived fuel.
"Refuse-derived fuel stoker" means a steam generating unit that combusts refuse-derived fuel in a semisuspension firing mode using air-fed distributors.
"Same location" means the same or contiguous property that is under common ownership or control including properties that are separated only by a street, road, highway, or other public right-of-way. Common ownership or control includes properties that are owned, leased, or operated by the same entity, parent entity, subsidiary, subdivision, or any combination thereof including any municipality or other governmental unit, or any quasi-governmental authority (e.g., a public utility district or regional waste disposal authority).
"Second calendar half" means the period starting July 1 and ending on December 31 in any year.
"Shift supervisor" means the person who is in direct charge and control of the operation of a municipal waste combustor and who is responsible for onsite supervision, technical direction, management, and overall performance of the facility during an assigned shift.
"Spreader stoker coal/refuse-derived fuel mixed fuel-fired combustor" means a combustor that fires coal and refuse-derived fuel simultaneously, in which coal is introduced to the combustion zone by a mechanism that throws the fuel onto a grate from above. Combustion takes place both in suspension and on the grate.
"Standard conditions" means a temperature of 20 degrees Centigrade and a pressure of 101.3 kilopascals.
"Total mass dioxin/furan" or "total mass" means the total mass of tetra- through octa- chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans, as determined using Reference Method 23 and the procedures specified under 9VAC5-40-8140 F.
"Tumbling-tile" means a grate tile hinged at one end and attached to a ram at the other end. When the ram extends, the grate tile rotates around the hinged edge.
"Twenty-four-hour daily average" means either the arithmetic mean or geometric mean (as specified) of all hourly emission concentrations when the affected facility is operating and combusting municipal solid waste measured over a 24-hour period between midnight and the following midnight.
"Untreated lumber" means wood or wood products that have been cut or shaped and include wet, air-dried, and kiln-dried wood products. Untreated lumber does not include wood products that have been painted, pigment-stained, or "pressure-treated." Pressure-treating compounds include, but are not limited to, chromate copper arsenate, pentachlorophenol, and creosote.
"Waterwall furnace" means a combustion unit having energy (heat) recovery in the furnace (i.e., radiant heat transfer section) of the combustor.
"Yard waste" means grass, grass clippings, bushes, shrubs, and clippings from bushes and shrubs that are generated by residential, commercial/retail, institutional, and industrial sources, or combination thereof, as part of maintenance activities associated with yards or other private or public lands. Yard waste does not include construction, renovation, and demolition wastes, which are exempt from the definition of municipal solid waste in this section. Yard waste does not include clean wood, which is exempt from the definition of municipal solid waste in this section.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999; amended, Virginia Register Volume 19, Issue 17, eff. July 1, 2003.
9VAC5-40-7970. Standard for particulate matter.
No owner or other person shall cause or permit to be discharged into the atmosphere from any affected facility any gases that contain particulate matter in excess of 27 milligrams per dry standard cubic meter, corrected to 7.0% oxygen.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999.
9VAC5-40-7980. Standard for carbon monoxide.
No owner or other person shall cause or permit to be discharged into the atmosphere from any affected facility any gases that contain carbon monoxide in excess of the following limits:
1. For mass burn waterwall units: 100 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis, calculated as an arithmetic average (four-hour average).
2. For mass burn refractory units: 100 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis, calculated as an arithmetic average (four-hour average).
3. For mass burn rotary refractory units: 100 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis, calculated as an arithmetic average (24-hour average).
4. For mass burn rotary waterwall units: 250 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis, calculated as an arithmetic average (24-hour average).
5. For modular starved air units: 50 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis, calculated as an arithmetic average (four-hour average).
6. For modular excess air units: 50 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis, calculated as an arithmetic average (four-hour average).
7. For refuse-derived fuel stokers: 200 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis, calculated as an arithmetic average (24-hour average).
8. For bubbling fluidized bed combustors: 100 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis, calculated as an arithmetic average (four-hour average).
9. For circulating fluidized bed combustors: 100 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis, calculated as an arithmetic average (four-hour average).
10. For pulverized coal/refuse-derived fuel mixed fuel-fired combustors: 150 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis, calculated as an arithmetic average (four-hour average).
11. For spreader stoker coal/refuse-derived fuel mixed fuel-fired combustors: 200 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis, calculated as an arithmetic average (24-hour average).
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999.
9VAC5-40-7990. Standard for cadmium.
No owner or other person shall cause or permit to be discharged into the atmosphere from any affected facility any gases that contain cadmium in excess of 0.040 milligrams per dry standard cubic meter, corrected to 7.0% oxygen.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999.
9VAC5-40-8000. Standard for lead.
No owner or other person shall cause or permit to be discharged into the atmosphere from any affected facility any gases that contain lead in excess of 0.44 milligrams per dry standard cubic meter, corrected to 7.0% oxygen.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999.
9VAC5-40-8010. Standard for mercury.
No owner or other person shall cause or permit to be discharged into the atmosphere from any affected facility any gases that contain mercury in excess of 0.080 milligrams per dry standard cubic meter or 15% of the potential mercury emission concentration (85% reduction by weight), corrected to 7.0% oxygen, whichever is less stringent.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999.
9VAC5-40-8020. Standard for sulfur dioxide.
No owner or other person shall cause or permit to be discharged into the atmosphere from any affected facility any gases that contain sulfur dioxide in excess of 29 parts per million by volume or 25% of the potential sulfur dioxide emission concentration (75% reduction by weight or volume), corrected to 7.0% oxygen (dry basis), whichever is less stringent. Compliance with this emission limit is based on a 24-hour daily geometric mean.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999.
9VAC5-40-8030. Standard for hydrogen chloride.
No owner or other person shall cause or permit to be discharged into the atmosphere from any affected facility any gases that contain hydrogen chloride in excess of 29 parts per million by volume or 5.0% of the potential hydrogen chloride emission concentration (95% reduction by weight or volume), corrected to 7.0% oxygen (dry basis), whichever is less stringent.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999.
9VAC5-40-8040. Standard for dioxin/furan.
No owner or other person shall cause or permit to be discharged into the atmosphere from any affected facility any gases that contain municipal waste combustor organics, expressed as total mass dioxins/furans, in excess of the following limits:
1. For facilities that employ an electrostatic precipitator-based emission control system, 60 nanograms per dry standard cubic meter (total mass), corrected to 7.0% oxygen.
2. For facilities that do not employ an electrostatic precipitator-based emission control system, 30 nanograms per dry standard cubic meter (total mass), corrected to 7.0% oxygen.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999.
9VAC5-40-8050. Standard for nitrogen oxides.
No owner or other person shall cause or permit to be discharged into the atmosphere from any affected facility any gases that contain nitrogen oxides in excess of the following limits:
1. For facilities not engaged in an emissions averaging plan as described in 9VAC5-40-8100 D:
a. For mass burn waterwall units: 205 parts per million by volume corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis.
b. For mass burn rotary waterwall units: 250 parts per million by volume corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis.
c. For refuse-derived fuel combustors: 250 parts per million by volume corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis.
d. For fluidized bed combustors: 180 parts per million by volume corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis.
e. For mass burn refractory combustors: no limit.
2. For facilities engaged in an emissions averaging plan as described in 9VAC5-40-8100 D:
a. For mass burn waterwall units: 185 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis.
b. For mass burn rotary waterwall units: 220 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis.
c. For refuse-derived fuel combustors: 230 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis.
d. For fluidized bed combustors: 165 parts per million by volume, corrected to 7.0% oxygen, dry basis.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999.
9VAC5-40-8060. Standard for visible emissions.
A. The provisions of Article 1 (9VAC5-40-60 et seq.) of 9VAC5 Chapter 40 (Emission Standards for Visible Emissions and Fugitive Dust/Emissions, Rule 4-1) apply except that the provisions in subsections B and C of this section apply instead of 9VAC5-40-80.
B. No owner or other person shall cause or permit to be discharged into the atmosphere from any affected facility any gases that exhibit greater than 10% opacity (6-minute average).
C. The owner of an air curtain incinerator with the capacity to combust greater than 250 tons per day of municipal solid waste and that combusts a fuel feed stream composed of 100% yard waste and no other municipal solid waste materials shall at no time cause to be discharged into the atmosphere from that incinerator any gases that exhibit greater than 10% opacity (6-minute average), except that an opacity level of up to 35% (6-minute average) is permitted during startup periods during the first 30 minutes of operation of the unit.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999.
9VAC5-40-8070. Standard for fugitive dust/emissions.
A. The provisions of Article 1 (9VAC5-40-60 et seq.) of 9VAC5 Chapter 40 (Emission Standards for Visible Emissions and Fugitive Dust/Emissions, Rule 4-1) apply except as provided in subsections B through D of this section.
B. No owner or other person shall cause to be discharged to the atmosphere visible emissions of combustion ash from an ash conveying system (including conveyor transfer points) in excess of 5.0% of the observation period (i.e., 9 minutes per 3-hour period), as determined by Reference Method 22 observations as specified in 9VAC5-40-8140 H, except as provided in subsections C and D of this section.
C. The emission limit specified in subsection B of this section shall not cover visible emissions discharged inside buildings or enclosures of ash conveying systems; however, the emission limit specified in subsection B of this section shall cover visible emissions discharged to the atmosphere from buildings or enclosures of ash conveying systems.
D. The provisions specified in subsection B of this section shall not apply during maintenance and repair of ash conveying systems.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999.
9VAC5-40-8080. Standard for odor.
The provisions of Article 2 (9VAC5-40-130 et seq.) of 9VAC5 Chapter 40 (Emission Standards for Odor, Rule 4-2) apply.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999.
9VAC5-40-8090. Standard for toxic pollutants.
The provisions of Article 4 (9VAC5-60-200 et seq.) of 9VAC5 Chapter 60 (Emission Standards for Toxic Pollutants, Rule 6-4) apply.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999; amended, Virginia Register Volume 19, Issue 17, eff. July 1, 2003.
9VAC5-40-8100. Compliance.
A. The provisions governing compliance shall be as follows:
1. With regard to the emissions standards in 9VAC5-40-8080 and 9VAC5-40-8090, the provisions of 9VAC5-40-20 (Compliance), apply.
2. With regard to the emission limits in 9VAC5-40-7970 through 9VAC5-40-8070, the following provisions apply:
a. 9VAC5-40-20 B, C, D, and E.
b. 40 CFR 60.11.
c. Subsections B through F of this section.
B. The provisions for startup, shutdown, and malfunction in subdivisions 1 and 2 of this subsection apply. Test methods and procedures for determining compliance shall be performed as specified in 9VAC5-40-8140.
1. Except as provided by 9VAC5-40-8060 C, the standards under this article apply at all times except during periods of startup, shutdown, or malfunction. Duration of startup, shutdown, or malfunction periods are limited to three hours per occurrence, except as provided in subdivision 1 c of this subsection.
a. The startup period commences when the affected facility begins the continuous burning of municipal solid waste and does not include any warmup period when the affected facility is combusting fossil fuel or other nonmunicipal solid waste fuel, and no municipal solid waste is being fed to the combustor.
b. Continuous burning is the continuous, semicontinuous, or batch feeding of municipal solid waste for purposes of waste disposal, energy production, or providing heat to the combustion system in preparation for waste disposal or energy production. The use of municipal solid waste solely to provide thermal protection of the grate or hearth during the startup period when municipal solid waste is not being fed to the grate is not considered to be continuous burning.
c. For the purpose of compliance with the carbon monoxide emission limits in 9VAC5-40-7980, if a loss of boiler water level control (e.g., boiler waterwall tube failure) or a loss of combustion air control (e.g., loss of combustion air fan, induced draft fan, combustion grate bar failure) is determined to be a malfunction, the duration of the malfunction period is limited to 15 hours per occurrence.
2. The opacity limits for air curtain incinerators specified in 9VAC5-40-8060 apply at all times as specified under 9VAC5-40-8060 except during periods of malfunction. Duration of malfunction periods are limited to three hours per occurrence.
C. The procedures specified in subdivisions 1 and 2 of this subsection shall be used for calculating municipal waste combustor unit capacity.
1. For municipal waste combustor units capable of combusting municipal solid waste continuously for a 24-hour period, municipal waste combustor unit capacity shall be calculated based on 24 hours of operation at the maximum charging rate. The maximum charging rate shall be determined as specified in subdivisions 1 a and 1 b of this subsection as applicable.
a. For combustors that are designed based on heat capacity, the maximum charging rate shall be calculated based on the maximum design heat input capacity of the unit and a heating value of 12,800 kilojoules per kilogram for combustors firing refuse-derived fuel and a heating value of 10,500 kilojoules per kilogram for combustors firing municipal solid waste that is not refuse-derived fuel.
b. For combustors that are not designed based on heat capacity, the maximum charging rate shall be the maximum design charging rate.
2. For batch feed municipal waste combustor units, municipal waste combustor unit capacity shall be calculated as the maximum design amount of municipal solid waste that can be charged per batch multiplied by the maximum number of batches that could be processed in a 24-hour period. The maximum number of batches that could be processed in a 24-hour period is calculated as 24 hours divided by the design number of hours required to process one batch of municipal solid waste, and may include fractional batches (e.g., if one batch requires 16 hours, then 24/16, or 1.5 batches, could be combusted in a 24-hour period). For batch combustors that are designed based on heat capacity, the design heating value of 12,800 kilojoules per kilogram for combustors firing refuse-derived fuel and a heating value of 10,500 kilojoules per kilogram for combustors firing municipal solid waste that is not refuse-derived fuel.
D. Nitrogen oxides emissions averaging is allowed as specified in this subsection.
1. The owner of a municipal waste combustor plant may elect to implement a nitrogen oxides emissions averaging plan for the affected facilities that are located at that plant and that are subject to this article, except as specified in subdivisions 1 a and 1 b of this subsection.
a. Municipal waste combustor units subject to subpart Ea or subpart Eb of 40 CFR Part 60 cannot be included in the emissions averaging plan.
b. Mass burn refractory municipal waste combustor units and other municipal waste combustion technologies not listed in 9VAC5-40-8050 B cannot be included in the emissions averaging plan.
2. The affected facilities included in the nitrogen oxides emissions averaging plan must be identified in the initial compliance report specified in 9VAC5-40-8160 J or in the annual report specified in 9VAC5-40-8160 D, as applicable, prior to implementing the averaging plan. The affected facilities being included in the averaging plan may be redesignated each calendar year. Partial year redesignation is allowable with board approval.
3. To implement the emissions averaging plan, the average daily (24-hour) nitrogen oxides emission concentration level for gases discharged from the affected facilities being included in the emissions averaging plan must be no greater than the levels specified in 9VAC5-40-8050 B.
4. Under the emissions averaging plan, the average daily nitrogen oxides emissions specified in 9VAC5-40-8050 B shall be calculated using the following equation. Affected facilities that are offline shall not be included in calculating the average daily nitrogen oxides emission level.
For Compliance, see Virginia Administrative Code print product.
5. For any day in which any affected facility included in the emissions averaging plan is offline, the owner of the municipal waste combustor plant must demonstrate compliance according to either subdivision 5 a of this subsection or both subdivisions 5 b and 5 c of this subsection.
a. Compliance with the applicable limits specified in 9VAC5-40-8050 B shall be demonstrated using the averaging procedure specified in subdivision 4 of this subsection for the affected facilities that are online.
b. For each of the affected facilities included in the emissions averaging plan, the nitrogen oxides emissions on a daily average basis shall be calculated and shall be equal to or less than the maximum daily nitrogen oxides emission level achieved by that affected facility on any of the days during which the emissions averaging plan was achieved with all affected facilities online during the most recent calendar quarter. The requirements of this subsection do not apply during the first quarter of operation under the emissions averaging plan.
c. The average nitrogen oxides emissions (kilograms per day) calculated according to subdivision 5 c (2) of this subsection shall not exceed the average nitrogen oxides emissions (kilograms per day) calculated according to subdivision 5 c (1) of this subsection.
(1) For all days during which the emissions averaging plan was implemented and achieved and during which all affected facilities were online, the average nitrogen oxides emissions shall be calculated. The average nitrogen oxides emissions (kilograms per day) shall be calculated on a calendar year basis according to subdivisions 5 c (1) (a) through 5 c (1) (c) of this subsection.
(a) For each affected facility included in the emissions averaging plan, the daily amount of nitrogen oxides emitted (kilograms per day) shall be calculated based on the hourly nitrogen oxides data specified under 9VAC5-40-8140 G 5, the flue gas flow rate determined using Table 19-1 of Reference Method 19 or a board-approved method, and the hourly average steam or feedwater flow rate.
(b) The daily total nitrogen oxides emissions shall be calculated as the sum of the daily nitrogen oxides emissions from each affected facility calculated under subdivision 5 c (1) (a) of this subsection.
(c) The average nitrogen oxides emissions (kilograms per day) on a calendar year basis shall be calculated as the sum of all daily total nitrogen oxides emissions calculated under subdivision 5 c (1) (b) of this subsection divided by the number of calendar days for which a daily total was calculated.
(2) For all days during which one or more of the affected facilities under the emissions averaging plan was offline, the average nitrogen oxides emissions shall be calculated. The average nitrogen oxides emissions (kilograms per day) shall be calculated on a calendar year basis according to subdivisions 5 c (2) (a) through 5 c (2) (c) of this subsection.
(a) For each affected facility included in the emissions averaging plan, the daily amount of nitrogen oxides emitted (kilograms per day) shall be calculated based on the hourly nitrogen oxides data specified under 9VAC5-40-8140 G 5, the flue gas flow rate determined using Table 19-1 of Reference Method 19, and the hourly average steam or feedwater flow rate.
(b) The daily total nitrogen oxides emissions shall be calculated as the sum of the daily nitrogen oxides emissions from each affected facility calculated under subdivision 5 c (2) (a) of this subsection.
(c) The average nitrogen oxides emissions (kilograms per day) on a calendar year basis shall be calculated as the sum of all daily total nitrogen oxides emissions calculated under subdivision 5 c (2) (b) of this subsection divided by the number of calendar days for which a daily total was calculated.
E. Owners of municipal waste combustor plants may engage in trading of nitrogen oxides emission credits. A trading program must be approved by the board before implementation.
F. The initial emission test shall be completed within 180 days after the final compliance date specified in 9VAC5-40-8110 A.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999; amended, Virginia Register Volume 19, Issue 17, eff. July 1, 2003.
9VAC5-40-8110. Compliance schedules.
A. The compliance schedule provisions of 40 CFR 62.14108 (40 CFR, July 1, 2002) and 40 CFR 62.14109(e) through (m) (40 CFR, July 1, 2002) apply.
B. All affected sources shall comply with the municipal waste combustor operator training and certification requirements under 9VAC5-40-8130 according to the schedule specified in subdivisions 1 and 2 of this subsection.
1. Affected facilities shall comply with the municipal waste combustor operator training and certification requirements specified in 9VAC5-40-8130 A through D by August 4, 2000.
2. Affected facilities shall comply with the requirements specified in 9VAC5-40-8130 E through H no later than August 4, 2000.
a. The requirement specified in 9VAC5-40-8130 E does not apply to chief facility operators, shift supervisors, and control room operators who have obtained full certification from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers on or before the effective date of this article.
b. The owner of an affected facility may request that the board waive the requirement specified in 9VAC5-40-8130 E for chief facility operators, shift supervisors, and control room operators who have obtained provisional certification from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers on or before the effective date of this article.
c. The initial training requirements specified in 9VAC5-40-8130 G 1 shall be completed no later than the date specified in subdivision 2 c (1) or 2 c (2) of this subsection, whichever is later.
(1) August 4, 2000; or
(2) The date prior to the day when the person assumes responsibilities affecting municipal waste combustor unit operation.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999; amended, Virginia Register Volume 19, Issue 17, eff. July 1, 2003.
9VAC5-40-8120. Operating practices.
A. No owner of an affected facility shall cause such facility to operate at a load level greater than 110% of the maximum demonstrated municipal waste combustor unit load, except as specified in subdivisions 1 and 2 of this subsection. The averaging time is specified under 9VAC5-40-8150 C.
1. During the annual dioxin/furan emission test and the two weeks preceding the annual dioxin/furan emission test, no municipal waste combustor unit load limit is applicable.
2. The municipal waste combustor unit load limit may be waived in accordance with permission granted by the board for the purpose of evaluating system performance, testing new technology or control technologies, diagnostic testing, or related activities for the purpose of improving facility performance or advancing the state-of-the-art for controlling facility emissions.
B. No owner of an affected facility shall cause such facility to operate at a temperature, measured at the particulate matter control device inlet, exceeding 17 degrees Centigrade above the maximum demonstrated particulate matter control device temperature as defined in 9VAC5-40-7960, except as specified in subdivisions 1 and 2 of this subsection. The averaging time is specified under 9VAC5-40-8150 C. The requirements specified in this subsection apply to each particulate matter control device utilized at the affected facility.
1. During the annual dioxin/furan emission test and the two weeks preceding the annual dioxin/furan emission test, no particulate matter control device temperature limitations are applicable.
2. The particulate matter control device temperature limits may be waived in accordance with permission granted by the board for the purpose of evaluating system performance, testing new technology or control technologies, diagnostic testing, or related activities for the purpose of improving facility performance or advancing the state-of-the-art for controlling facility emissions.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999; amended, Virginia Register Volume 19, Issue 17, eff. July 1, 2003.
9VAC5-40-8130. Operator training and certification.
A. Each chief facility operator and shift supervisor of an affected facility shall obtain and maintain a current provisional operator training certification from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers as provided in the "Standard for the Qualification and Certification of Resource Recovery Facility Operators" (see 9VAC5-20-21) or a board-approved certification program.
B. Each chief facility operator and shift supervisor of an affected facility shall have completed full certification or scheduled a full certification exam with either the American Society of Mechanical Engineers as provided in the "Standard for the Qualification and Certification of Resource Recovery Facility Operators" (see 9VAC5-20-21) or a board-approved certification program.
C. No owner of an affected facility shall allow the facility to be operated at any time unless a person is on duty who is responsible for the proper operation of the facility and has a license from the Board for Waste Management Facility Operators in the correct classification. No provision of this article shall relieve any owner from the responsibility to comply in all respects with the requirements of Chapter 22.1 (§ 54.1-2209 et seq.) of Title 54.1 of the Code of Virginia, and with 18VAC155 Chapter 20.
D. No owner of an affected facility shall allow the facility to be operated at any time unless one of the following persons is on duty and at the affected facility: a fully certified chief facility operator, a provisionally certified chief facility operator who is scheduled to take the full certification exam according to the schedule specified in 9VAC5-40-8110 B 1, a fully certified shift supervisor, or a provisionally certified shift supervisor who is scheduled to take the full certification exam according to the schedule specified in 9VAC5-40-8110 B 1.
If one of the persons listed in this subsection must leave the affected facility during that person's operating shift, a provisionally certified control room operator who is onsite at the affected facility may fulfill the requirement in this subsection.
E. All chief facility operators, shift supervisors, and control room operators at affected facilities must complete the board-approved municipal waste combustor operator training course.
F. The owner of an affected facility shall develop and update on a yearly basis a site-specific operating manual that shall, at a minimum, address the elements of municipal waste combustor unit operation specified in this subsection.
1. A summary of the applicable standards under this article;
2. A description of basic combustion theory applicable to a municipal waste combustor unit;
3. Procedures for receiving, handling, and feeding municipal solid waste;
4. Municipal waste combustor unit startup, shutdown, and malfunction procedures;
5. Procedures for maintaining proper combustion air supply levels;
6. Procedures for operating the municipal waste combustor unit within the standards established under this article;
7. Procedures for responding to periodic upset or off-specification conditions;
8. Procedures for minimizing particulate matter carryover;
9. Procedures for handling ash;
10. Procedures for monitoring municipal waste combustor unit emissions; and
11. Reporting and recordkeeping procedures.
G. The owner of an affected facility shall establish a training program to review the operating manual according to the schedule specified in this subsection with each person who has responsibilities affecting the operation of an affected facility including, but not limited to, chief facility operators, shift supervisors, control room operators, ash handlers, maintenance personnel, and crane/load handlers.
1. Each person specified in this subsection shall undergo initial training no later than the date specified in subdivision 1 a or 1 b of this subsection, whichever is later.
a. The date prior to the day the person assumes responsibilities affecting municipal waste combustor unit operation; or
b. August 4, 2000.
2. Each person specified in this subsection shall undergo initial training annually, following the initial review required by subdivision 1 of this subsection.
H. The operating manual required by subsection F of this section shall be kept in a readily accessible location for all persons required to undergo training under subsection G of this section. The operating manual and records of training shall be available for inspection by the board upon request.
I. The requirements of subsections A and B of this section with regard to obtaining operator training certification through a program approved by the board may be met by obtaining a license from the Board for Waste Management Facility Operators. All training and licensing shall be conducted in accordance with Chapter 22.1 (§ 54.1-2209 et seq.) of Title 54.1 of the Code of Virginia, and with 18VAC155 Chapter 20.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999; amended, Virginia Register Volume 18, Issue 7, eff. February 1, 2002; Volume 19, Issue 17, eff. July 1, 2003.
9VAC5-40-8140. Test methods and procedures.
A. The provisions governing test methods and procedures shall be as follows:
1. With regard to the emissions standards in 9VAC5-40-8080 and 9VAC5-40-8090, the provisions of 9VAC5-40-30 (Emission testing) apply.
2. With regard to the emission limits in 9VAC5-40-7970 through 9VAC5-40-8070, the following provisions apply:
a. 9VAC5-40-30 D and G.
b. 40 CFR 60.8, with the exception of paragraph (a).
c. 40 CFR 60.11 and 40 CFR 60.13.
d. Subsections B through J of this section.
B. The procedures and test methods specified in this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with the emission limits for particulate matter and opacity under 9VAC5-40-7970 and 9VAC5-40-8060.
1. Reference Method 1 shall be used to select sampling site and number of traverse points.
2. Reference Method 3, 3A, or 3B, as applicable, shall be used for gas analysis.
3. Reference Method 5 shall be used for determining compliance with the particulate matter emission limit. The minimum sample volume shall be 1.7 cubic meters. The probe and filter holder heating systems in the sample train shall be set to provide a gas temperature no greater than 160 ± 14 degrees Centigrade. An oxygen or carbon dioxide measurement shall be obtained simultaneously with each Reference Method 5 run.
4. The owner of an affected facility may request that compliance with the particulate matter emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 B 6.
5. As specified in 40 CFR 60.8, all emission tests shall consist of three test runs. The average of the particulate matter emission concentrations from the three test runs is used to determine compliance.
6. In accordance with subdivisions 7 and 10 of this subsection, Reference Method 9 shall be used for determining compliance with the opacity limit except as provided in 40 CFR 60.11(e).
7. The owner of an affected facility shall conduct an initial emission test for particulate matter emissions and opacity as required in 9VAC5-40-8100.
8. The owner of an affected facility shall install, calibrate, maintain, and operate a continuous opacity monitoring system for measuring opacity and shall follow the methods and procedures specified in subdivisions 8 a through 8 d of this subsection.
a. The output of the continuous opacity monitoring system shall be recorded on a 6-minute average basis.
b. The continuous opacity monitoring system shall be installed, evaluated, and operated in accordance with 40 CFR 60.13.
c. The continuous opacity monitoring system shall conform to Performance Specification 1 in Appendix B of 40 CFR Part 60.
d. The initial performance evaluation shall be completed as specified in 9VAC5-40-8100.
9. Following the date that the initial emission test for particulate matter is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100 for an affected facility, the owner shall conduct an emission test for particulate matter on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months following the previous emission test).
10. Following the date that the initial emission test for opacity is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100 for an affected facility, the owner shall conduct an emission test for opacity on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months following the previous emission test) using the test method specified in subdivision 6 of this subsection.
C. The procedures and test methods specified in this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with the emission limits for cadmium, lead, and mercury under 9VAC5-40-7990, 9VAC5-40-8000, and 9VAC5-40-8010.
1. The procedures and test methods specified in subdivisions 1 a through 1 g of this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with the emission limits for cadmium and lead under 9VAC5-40-7990 and 9VAC5-40-8000.
a. Reference Method 1 shall be used for determining the location and number of sampling points.
b. Reference Method 3, 3A, or 3B, as applicable, shall be used for flue gas analysis.
c. Reference Method 29 shall be used for determining compliance with the cadmium and lead emission limits.
d. An oxygen or carbon dioxide measurement shall be obtained simultaneously with each Reference Method 29 test run for cadmium and lead required under subdivision 1 c of this subsection.
e. The owner of an affected facility may request that compliance with the cadmium or lead emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 B 6.
f. All emission tests shall consist of a minimum of three test runs conducted under representative full load operating conditions. The average of the cadmium or lead emission concentrations from three test runs or more shall be used to determine compliance.
g. Following the date of the initial emission test or the date on which the initial emission test is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100, the owner of an affected facility shall conduct an emission test for compliance with the emission limits for cadmium and lead on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months following the previous emission test).
2. The procedures and test methods specified in subdivisions 2 a through 2 j of this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with the mercury emission limit under 9VAC5-40-8010.
a. Reference Method 1 shall be used for determining the location and number of sampling points.
b. Reference Method 3, 3A, or 3B, as applicable, shall be used for flue gas analysis.
c. Reference Method 29 shall be used to determine the mercury emission concentration. The minimum sample volume when using Reference Method 29 for mercury shall be 1.7 cubic meters.
d. An oxygen (or carbon dioxide) measurement shall be obtained simultaneously with each Reference Method 29 test run for mercury required under subdivision 2 c of this subsection.
e. The percent reduction in the potential mercury emissions (% pHg) is computed using the following equation:
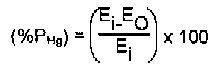
where:
%PHg = percent reduction of the potential mercury emissions achieved.
Ei = potential mercury emission concentration measured at the control device inlet, corrected to 7.0% oxygen (dry basis).
EO = controlled mercury emission concentration measured at the mercury control device outlet, corrected to 7.0% oxygen (dry basis).
f. All emission tests shall consist of a minimum of three test runs conducted under representative full load operating conditions. The average of the mercury emission concentrations or percent reductions from three test runs or more is used to determine compliance.
g. The owner of an affected facility may request that compliance with the mercury emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 B 6.
h. The owner of an affected facility shall conduct an initial emission test for mercury emissions as required in 9VAC5-40-8100.
i. Following the date that the initial emission test for mercury is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100, the owner of an affected facility shall conduct an emission test for mercury emissions on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months from the previous emission test).
j. The owner of an affected facility where activated carbon injection is used to comply with the mercury emission limit shall follow the procedures specified in subsection J of this section for measuring and calculating carbon usage.
D. The procedures and test methods specified in this subsection shall be used for determining compliance with the sulfur dioxide emission limit under 9VAC5-40-8020.
1. Reference Method 19, section 4.3, shall be used to calculate the daily geometric average sulfur dioxide emission concentration.
2. Reference Method 19, section 5.4, shall be used to determine the daily geometric average percent reduction in the potential sulfur dioxide emission concentration.
3. The owner of an affected facility may request that compliance with the sulfur dioxide emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 B 6.
4. The owner of an affected facility shall conduct an initial emission test for sulfur dioxide emissions as required in 9VAC5-40-8100. Compliance with the sulfur dioxide emission limit (concentration or percent reduction) shall be determined by using the continuous emission monitoring system specified in subdivision 5 of this subsection to measure sulfur dioxide and calculating a 24-hour daily geometric average emission concentration or a 24-hour daily geometric average percent reduction using Reference Method 19, sections 4.3 and 5.4, as applicable.
5. The owner of an affected facility shall install, calibrate, maintain, and operate a continuous emission monitoring system for measuring sulfur dioxide emissions discharged to the atmosphere and record the output of the system.
6. Following the date that the initial emission test for sulfur dioxide is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100, compliance with the sulfur dioxide emission limit shall be determined based on the 24-hour daily geometric average of the hourly arithmetic average emission concentrations using continuous emission monitoring system outlet data if compliance is based on an emission concentration, or continuous emission monitoring system inlet and outlet data if compliance is based on a percent reduction.
7. At a minimum, valid continuous monitoring system hourly averages shall be obtained as specified in subdivisions 7 a and 7 b of this subsection for 75% of the operating hours per day for 90% of the operating days per calendar quarter that the affected facility is combusting municipal solid waste.
a. At least two data points per hour shall be used to calculate each one-hour arithmetic average.
b. Each sulfur dioxide one-hour arithmetic average shall be corrected to 7.0% oxygen on an hourly basis using the one-hour arithmetic average of the oxygen (or carbon dioxide) continuous emission monitoring system data.
8. The one-hour arithmetic averages required under subdivision 6 of this subsection shall be expressed in parts per million corrected to 7.0% oxygen (dry basis) and used to calculate the 24-hour daily geometric average emission concentrations and daily geometric average emission percent reductions. The one-hour arithmetic averages shall be calculated using the data points required in 40 CFR 60.13(e)(2).
9. All valid continuous emission monitoring system data shall be used in calculating average emission concentrations and percent reductions even if the minimum continuous emission monitoring system data requirements of subdivision 7 of this subsection are not met.
10. The procedures in 40 CFR 60.13 shall be followed for installation, evaluation, and operation of the continuous emission monitoring system.
11. The initial performance evaluation shall be completed as specified in 9VAC5-40-8100.
12. The continuous emission monitoring system shall be operated according to Performance Specification 2 in Appendix B of 40 CFR Part 60.
a. During each relative accuracy test run of the continuous emission monitoring system required by Performance Specification 2 in Appendix B of 40 CFR Part 60, sulfur dioxide and oxygen (or carbon dioxide) data shall be collected concurrently (or within a 30- to 60-minute period) by both the continuous emission monitors and the test methods specified in subdivisions 12 a (1) and 12 a (2) of this subsection.
(1) For sulfur dioxide, Reference Method 6, 6A, or 6C shall be used.
(2) For oxygen (or carbon dioxide), Reference Method 3, 3A, or 3B, as applicable, shall be used.
b. The span value of the continuous emissions monitoring system at the inlet to the sulfur dioxide control device shall be 125% of the maximum estimated hourly potential sulfur dioxide emissions of the municipal waste combustor unit. The span value of the continuous emission monitoring system at the outlet of the sulfur dioxide control device shall be 50% of the maximum estimated hourly potential sulfur dioxide emissions of the municipal waste combustor unit.
13. Quarterly accuracy determinations and daily calibration drift tests shall be performed in accordance with procedure 1 in Appendix F of 40 CFR Part 60.
14. When sulfur dioxide emissions data are not obtained because of continuous emission monitoring system breakdowns, repairs, calibration checks, and zero and span adjustments, emissions data shall be obtained by using other monitoring systems as approved by the board or Reference Method 19 to provide, as necessary, valid emissions data for a minimum of 75% of the hours per day that the affected facility is operated and combusting municipal solid waste for 90% of the days per calendar quarter that the affected facility is operated and combusting municipal solid waste.
E. The procedures and test methods specified in this subsection shall be used for determining compliance with the hydrogen chloride emission limit under 9VAC5-40-8030.
1. Reference Method 26 or 26A, as applicable, shall be used to determine the hydrogen chloride emission concentration. The minimum sampling time for Reference Method 26 shall be one hour.
2. An oxygen (or carbon dioxide) measurement shall be obtained simultaneously with each Reference Method 26 test run for hydrogen chloride required by subdivision 1 of this subsection.
3. The percent reduction in potential hydrogen chloride emissions (%PHCl) is computed using the following equation:

where:
%PHCl = percent reduction of the potential hydrogen chloride emissions achieved.
Ei = potential hydrogen chloride emission concentration measured at the control device inlet, corrected to 7.0% oxygen (dry basis).
EO = controlled hydrogen chloride emission concentration measured at the control device outlet, corrected to 7.0% oxygen (dry basis).
4. The owner of an affected facility may request that compliance with the hydrogen chloride emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 B 6.
5. As specified in 40 CFR 60.8, all emission tests shall consist of three test runs. The average of the hydrogen chloride emission concentrations or percent reductions from the three test runs is used to determine compliance.
6. The owner of an affected facility shall conduct an initial emission test for hydrogen chloride as required in 9VAC5-40-8100.
7. Following the date that the initial emission test for hydrogen chloride is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100, the owner of an affected facility shall conduct an emission test for hydrogen chloride emissions on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months following the previous emission test).
F. The procedures and test methods specified in this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with the limits for dioxin/furan emissions under 9VAC5-40-8040.
1. Reference Method 1 shall be used for determining the location and number of sampling points.
2. Reference Method 3, 3A, or 3B, as applicable, shall be used for flue gas analysis.
3. Reference Method 23 shall be used for determining the dioxin/furan emission concentration.
a. The minimum sample time shall be four hours per test run.
b. An oxygen (or carbon dioxide) measurement shall be obtained simultaneously with each Reference Method 23 test run for dioxins/furans.
4. The owner of an affected facility shall conduct an initial emission test for dioxin/furan emissions in accordance with subdivision 3 of this subsection, as required in 9VAC5-40-8100.
5. Following the date that the initial emission test for dioxins/furans is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100, the owner of an affected facility shall conduct emission tests for dioxin/furan emissions in accordance with subdivision 3 of this subsection, according to one of the schedules specified in subdivision 5 a or 5 b of this subsection.
a. For affected facilities, emission tests shall be conducted on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months following the previous emission test).
b. Where all emission tests over a two-year period indicate that dioxin/furan emissions are less than or equal to 15 nanograms per dry standard cubic meter (total mass) for all affected facilities located within a municipal waste combustor plant, the owner of the municipal waste combustor plant may elect to conduct annual emission tests for one affected facility (i.e., unit) per year at the municipal waste combustor plant. At a minimum, an emission test for dioxin/furan emissions shall be conducted annually (no more than 12 months following the previous emission test) for one affected facility at the municipal waste combustor plant. Each year a different affected facility at the municipal waste combustor plant shall be tested, and the affected facilities at the plant shall be tested in sequence (e.g., unit 1, unit 2, unit 3, as applicable). If each annual emission test continues to indicate a dioxin/furan emission level less than or equal to 15 nanograms per dry standard cubic meter (total mass), the owner may continue conducting an emission test on only one affected facility per year. If any annual emission test indicates a dioxin/furan emission level greater than 15 nanograms per dry standard cubic meter (total mass), emission tests thereafter shall be conducted annually on all affected facilities at the plant until and unless all annual emission tests for all affected facilities at the plant over a two-year period indicate a dioxin/furan emission level less than or equal to 15 nanograms per dry standard cubic meter (total mass).
6. The owner of an affected facility that selects to follow the emission testing schedule specified in subdivision 5 a or 5 b of this subsection shall follow the procedures specified in 9VAC5-40-8160 D 4 for reporting the selection of this schedule.
7. The owner of an affected facility where activated carbon is used to comply with the dioxin/furan emission limits specified in 9VAC5-40-8040 or the dioxin/furan emission level specified in subdivision 5 a or 5 b of this subsection shall follow the procedures specified in subsection J of this section for measuring and calculating the carbon usage rate.
8. The owner may request that compliance with the dioxin/furan emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 B 6.
9. As specified in 40 CFR 60.8, all emission tests shall consist of three test runs. The average of the dioxin/furan emission concentrations from the three test runs is used to determine compliance.
G. The procedures and test methods specified in this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with the nitrogen oxides emission limit for affected facilities under 9VAC5-40-8050.
1. Reference Method 19, section 4.1, shall be used for determining the daily arithmetic average nitrogen oxides emission concentration.
2. The owner of an affected facility may request that compliance with the nitrogen oxides emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in 9VAC5-40-8150 B 6.
3. The owner of an affected facility subject to the nitrogen oxides limit under 9VAC5-40-8050 shall conduct an initial emission test for nitrogen oxides as required in 9VAC5-40-8100. Compliance with the nitrogen oxides emission limit shall be determined by using the continuous emission monitoring system specified in subdivision 4 of this subsection for measuring nitrogen oxides and calculating a 24-hour daily arithmetic average emission concentration using Reference Method 19, section 4.1.
4. The owner of an affected facility subject to the nitrogen oxides emission limit under 9VAC5-40-8050 shall install, calibrate, maintain, and operate a continuous emission monitoring system for measuring nitrogen oxides discharged to the atmosphere, and record the output of the system.
5. Following the date that the initial emission test for nitrogen oxides is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100, compliance with the emission limit for nitrogen oxides required under 9VAC5-40-8050 shall be determined based on the 24-hour daily arithmetic average of the hourly emission concentrations using continuous emission monitoring system outlet data.
6. At a minimum, valid continuous emission monitoring system hourly averages shall be obtained as specified in subdivisions 6 a and 6 b of this subsection for 75% of the operating hours per day for 90% of the operating days per calendar quarter that the affected facility is combusting municipal solid waste.
a. At least two data points per hour shall be used to calculate each one-hour arithmetic average.
b. Each nitrogen oxides one-hour arithmetic average shall be corrected to 7.0% oxygen on an hourly basis using the one-hour arithmetic average of the oxygen (or carbon dioxide) continuous emission monitoring system data.
7. The one-hour arithmetic averages required by subdivision 5 of this subsection shall be expressed in parts per million by volume (dry basis) and used to calculate the 24-hour daily arithmetic average concentrations. The one-hour arithmetic averages shall be calculated using the data points required in 40 CFR 60.13(e)(2).
8. All valid continuous emission monitoring system data must be used in calculating emission averages even if the minimum continuous emission monitoring system data requirements of subdivision 6 of this subsection are not met.
9. The procedures in 40 CFR 60.13 shall be followed for installation, evaluation, and operation of the continuous emission monitoring system. The initial performance evaluation shall be completed as specified in 9VAC5-40-8100.
10. The owner of an affected facility shall operate the continuous emission monitoring system according to Performance Specification 2 in Appendix B of 40 CFR Part 60 and shall follow the procedures and methods specified in subdivisions 10 a and 10 b of this subsection.
a. During each relative accuracy test run of the continuous emission monitoring system required by Performance Specification 2 of Appendix B of 40 CFR Part 60, nitrogen oxides and oxygen (or carbon dioxide) data shall be collected concurrently (or within a 30- to 60-minute period) by both the continuous emission monitors and the test methods specified in subdivisions 10 a (1) and 10 a (2) of this subsection.
(1) For nitrogen oxides, Reference Method 7, 7A, 7C, 7D, or 7E shall be used.
(2) For oxygen (or carbon dioxide), Reference Method 3, 3A, or 3B, as applicable, shall be used.
b. The span value of the continuous emission monitoring system shall be 125% of the maximum estimated hourly potential nitrogen oxide emissions of the municipal waste combustor unit.
11. Quarterly accuracy determinations and daily calibration drift tests shall be performed in accordance with procedure 1 in Appendix F of 40 CFR Part 60.
12. When nitrogen oxides continuous emissions data are not obtained because of continuous emission monitoring system breakdowns, repairs, calibration checks, and zero and span adjustments, emissions data shall be obtained using other monitoring systems as approved by the board or Reference Method 19 to provide, as necessary, valid emissions data for a minimum of 75% of the hours per day for 90% of the days per calendar quarter the unit is operated and combusting municipal solid waste.
H. The procedures specified in this subsection shall be used for determining compliance with the fugitive ash emission limit under 9VAC5-40-8070.
1. Reference Method 22 shall be used for determining compliance with the fugitive ash emission limit under 9VAC5-40-8070. The minimum observation time shall be a series of three one-hour observations. The observation period shall include times when the facility is transferring ash from the municipal waste combustor unit to the area where ash is stored or loaded into containers or trucks.
2. The average duration of visible emissions per hour shall be calculated from the three one-hour observations. The average shall be used to determine compliance with 9VAC5-40-8070.
3. The owner of an affected facility shall conduct an initial emission test for fugitive ash emissions as required in 9VAC5-40-8100.
4. Following the date that the initial emission test for fugitive ash emissions is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100 for an affected facility, the owner shall conduct an emission test for fugitive ash emissions on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months following the previous emission test).
I. The procedures specified in this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with the opacity limit for air curtain incinerators under 9VAC5-40-8060 C.
1. Reference Method 9 shall be used for determining compliance with the opacity limit.
2. The owner of the air curtain incinerator shall conduct an initial emission test for opacity as required in 9VAC5-40-8100.
3. Following the date that the initial emission test is completed or is required to be completed in 9VAC5-40-8100, the owner of the air curtain incinerator shall conduct an emission test for opacity on an annual basis (no more than 12 calendar months following the previous emission test).
J. The owner of an affected facility where activated carbon injection is used to comply with the mercury emission limit under 9VAC5-40-8010, or the dioxin/furan emission limits under 9VAC5-40-8040, or the dioxin/furan emission level specified in subdivision F 5 b of this section shall follow the procedures specified in this subsection.
1. During the emission tests for dioxins/furans and mercury, as applicable, the owner shall estimate an average carbon mass feed rate based on carbon injection system operating parameters such as the screw feeder speed, hopper volume, hopper refill frequency, or other parameters appropriate to the feed system being employed, as specified in subdivisions 1 a and 1 b of this subsection.
a. An average carbon mass feed rate in kilograms per hour or pounds per hour shall be estimated during the initial emission test for mercury emissions and each subsequent emission test for mercury emissions.
b. An average carbon mass feed rate in kilograms per hour or pounds per hour shall be estimated during the initial emission test for dioxin/furan emissions and each subsequent emission test for dioxin/furan emissions.
2. During operation of the affected facility, the carbon injection system operating parameter(s) that are the primary indicator(s) of the carbon mass feed rate (e.g., screw feeder setting) must equal or exceed the level(s) documented during the emission tests specified under subdivisions 1 a and 1 b of this subsection.
3. The owner of an affected facility shall estimate the total carbon usage of the plant (kilograms or pounds) for each calendar quarter by two independent methods, according to the procedures in subdivisions 3 a and 3 b of this subsection.
a. The weight of carbon delivered to the plant.
b. Estimate the average carbon mass feed rate in kilograms per hour or pounds per hour for each hour of operation for each affected facility based on the parameters specified under subdivision 1 of this subsection, and sum the results for all affected facilities at the plant for the total number of hours of operation during the calendar quarter.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999; amended, Virginia Register Volume 19, Issue 17, eff. July 1, 2003.
9VAC5-40-8150. Monitoring.
A. The provisions governing monitoring shall be as follows:
1. With regard to the emissions standards in 9VAC5-40-8080 and 9VAC5-40-8090, the provisions of 9VAC5-40-40 (Monitoring) apply.
2.With regard to the emission limits in 9VAC5-40-7970 through 9VAC5-40-8070, the following provisions apply:
a. 9VAC5-40-40 A and F.
b. 40 CFR 60.13.
c. Subsections B and C of this section.
B. The owner of an affected facility shall install, calibrate, maintain, and operate a continuous emission monitoring system and record the output of the system for measuring the oxygen or carbon dioxide content of the flue gas at each location where carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, or nitrogen oxides emissions are monitored and shall comply with the test procedures and test methods specified in this subsection.
1. The span value of the oxygen (or carbon dioxide) monitor shall be 25% oxygen (or carbon dioxide).
2. The monitor shall be installed, evaluated, and operated in accordance with 40 CFR 60.13.
3. The initial performance evaluation shall be completed prior to the initial emission test as specified in 9VAC5-40-8100.
4. The monitor shall conform to Performance Specification 3 in Appendix B of 40 CFR Part 60 except for section 2.3 (relative accuracy requirement).
5. The quality assurance procedures of Appendix F of 40 CFR Part 60 except for section 5.1.1 (relative accuracy test audit) shall apply to the monitor.
6. If carbon dioxide is selected for use in diluent corrections, the relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels shall be established during the initial emission test according to the procedures and methods specified in subdivisions 6 a through 6 d of this subsection. This relationship may be reestablished during performance compliance tests.
a. The fuel factor equation in Reference Method 3B shall be used to determine the relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide at a sampling location. Reference method 3, 3A, or 3B, as applicable, shall be used to determine the oxygen concentration at the same location as the carbon dioxide monitor.
b. Samples shall be taken for at least 30 minutes in each hour.
c. Each sample shall represent a one-hour average.
d. A minimum of three runs shall be performed.
7. The relationship between carbon dioxide and oxygen concentrations that is established in accordance with subdivision 6 of this subsection shall be submitted to the board as part of the initial emission test report and, if applicable, as part of the annual test report if the relationship is reestablished during the annual emission test.
C. The procedures specified in this subsection shall be used for determining compliance with the operating requirements under 9VAC5-40-8120.
1. Compliance with the carbon monoxide emission limits in 9VAC5-40-7980 shall be determined using a four-hour block arithmetic average for all types of affected facilities except mass burn rotary waterwall municipal waste combustors and refuse-derived fuel stokers.
2. For affected mass burn rotary waterwall municipal waste combustors and refuse-derived fuel stokers, compliance with the carbon monoxide emission limits in 9VAC5-40-7980 shall be determined using a 24-hour daily arithmetic average.
3. The owner of an affected facility shall install, calibrate, maintain, and operate a continuous emission monitoring system for measuring carbon monoxide at the combustor outlet and record the output of the system and shall follow the procedures and methods specified in subdivisions 3 a through 3 c of this subsection.
a. The continuous emission monitoring system shall be operated according to Performance Specification 4A in Appendix B of 40 CFR Part 60.
b. During each relative accuracy test run of the continuous emission monitoring system required by Performance Specification 4A in Appendix B of 40 CFR Part 60, carbon monoxide and oxygen (or carbon dioxide) data shall be collected concurrently (or within a 30- to 60-minute period) by both the continuous emission monitors and the test methods specified in subdivisions 3 b (1) and 3 b (2) of this subsection.
(1) For carbon monoxide, Reference Method 10, 10A, or 10B shall be used.
(2) For oxygen (or carbon dioxide), Reference Method 3, 3A, or 3B, as applicable, shall be used.
c. The span value of the continuous emission monitoring system shall be 125% of the maximum estimated hourly potential carbon monoxide emissions of the municipal waste combustor unit.
4. The four-hour block and 24-hour daily arithmetic averages specified in subdivisions 1 and 2 of this subsection shall be calculated from one-hour arithmetic averages expressed in parts per million by volume corrected to 7.0% oxygen (dry basis). The one-hour arithmetic averages shall be calculated using the data points generated by the continuous emission monitoring system. At least two data points shall be used to calculate each one-hour arithmetic average.
5. The owner of an affected facility may request that compliance with the carbon monoxide emission limit be determined using carbon dioxide measurements corrected to an equivalent of 7.0% oxygen. The relationship between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels for the affected facility shall be established as specified in subdivision B 6 of this section.
6. The procedures specified in subdivisions 6 a through 6 d of this subsection shall be used to determine compliance with load level requirements under 9VAC5-40-8120 A.
a. The owner of an affected facility with steam generation capability shall install, calibrate, maintain, and operate a steam flow meter or a feedwater flow meter; measure steam (or feedwater) flow in kilograms per hour (or pounds per hour) on a continuous basis; and record the output of the monitor. Steam (or feedwater) flow shall be calculated in four-hour block arithmetic averages.
b. The method included in section 4 of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers publication, "Power Test Codes: Steam Generating Units" (see 9VAC5-20-21) shall be used for calculating the steam (or feedwater) flow required under subdivision 6 a of this subsection. The recommendations in chapter 4 of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers publication, "Interim Supplement 19.5 on Instruments and Apparatus: Application, Part II of Fluid Meters" (see 9VAC5-20-21) shall be followed for design, construction, installation, calibration, and use of nozzles and orifices except as specified in subdivision 6 c of this subsection.
c. Measurement devices such as flow nozzles and orifices are not required to be recalibrated after they are installed.
d. All signal conversion elements associated with steam (or feedwater flow) measurements must be calibrated according to the manufacturer's instructions before each dioxin/furan emission test, and at least once per year.
7. To determine compliance with the maximum particulate matter control device temperature requirements under 9VAC5-40-8120 B, the owner of an affected facility shall install, calibrate, maintain, and operate a device for measuring on a continuous basis the temperature of the flue gas stream at the inlet to each particulate matter control device utilized by the affected facility. Temperature shall be calculated in four-hour block arithmetic averages.
8. The maximum demonstrated municipal waste combustor unit load shall be determined during the initial emission test for dioxins/furans and each subsequent emission test during which compliance with the dioxin/furan emission limit specified in 9VAC5-40-8040 is achieved. The maximum demonstrated municipal waste combustor unit load shall be the highest four-hour arithmetic average load achieved during four consecutive hours during the most recent test during which compliance with the dioxin/furan emission limit was achieved.
9. For each particulate matter control device employed at the affected facility, the maximum demonstrated particulate matter control device temperature shall be determined during the initial emission test for dioxins/furans and each subsequent emission test during which compliance with the dioxin/furan emission limit specified in 9VAC5-40-8040 is achieved. The maximum demonstrated particulate matter control device temperature shall be the highest four-hour arithmetic average temperature achieved at the particulate matter control device inlet during four consecutive hours during the most recent test during which compliance with the dioxin/furan limit was achieved.
10. At a minimum, valid continuous emission monitoring system hourly averages shall be obtained as specified in subdivisions 10 a and 10 b of this subsection for 75% of the operating hours per day for 90% of the operating days per calendar quarter that the affected facility is combusting municipal solid waste.
a. At least two data points per hour shall be used to calculate each one-hour arithmetic average.
b. At a minimum, each carbon monoxide one-hour arithmetic average shall be corrected to 7.0% oxygen on an hourly basis using the one-hour arithmetic average of the oxygen (or carbon dioxide) continuous emission monitoring system data.
11. All valid continuous emission monitoring system data must be used in calculating the parameters specified under this section even if the minimum data requirements of subdivision 10 of this subsection are not met. When carbon monoxide continuous emission data are not obtained because of continuous emission monitoring system breakdowns, repairs, calibration checks, and zero and span adjustments, emissions data shall be obtained using other monitoring systems as approved by the board or Reference Method 10 to provide, as necessary, the minimum valid emission data.
12. Quarterly accuracy determinations and daily calibration drift tests for the carbon monoxide continuous emission monitoring system shall be performed in accordance with procedure 1 in Appendix F of 40 CFR Part 60.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999; amended, Virginia Register Volume 18, Issue 7, eff. February 1, 2002; Volume 19, Issue 17, eff. July 1, 2003.
9VAC5-40-8160. Notification, records and reporting.
A. The provisions governing notification, records and reporting shall be as follows:
1. With regard to the emissions standards in 9VAC5-40-8080 and 9VAC5-40-8090, the provisions of 9VAC5-40-50 (Notification, records and reporting) apply.
2. With regard to the emission limits in 9VAC5-40-7970 through 9VAC5-40-8070, the following provisions apply:
a. 9VAC5-40-50 F and H.
b. 40 CFR 60.7.
c. Subsections B through J of this section.
B. The owner of an affected facility shall maintain records of the information specified in this subsection, as applicable, for each affected facility for a period of at least five years.
1. The calendar date of each record.
2. The emission concentrations and parameters measured using continuous monitoring systems as specified under subdivisions 2 a and 2 b of this subsection.
a. The measurements specified in subdivisions 2 a (1) through 2 a (4) of this subsection shall be recorded and be available for submittal to the board or review onsite by an inspector.
(1) All six-minute average opacity levels as specified under 9VAC5-40-8140 B.
(2) All one-hour average sulfur dioxide emission concentrations as specified under 9VAC5-40-8140 D.
(3) All one-hour average nitrogen oxides emission concentrations as specified under 9VAC5-40-8140 G.
(4) All one-hour average carbon monoxide emission concentrations, municipal waste combustor unit load measurements, and particulate matter control device inlet temperatures as specified under 9VAC5-40-8150 C.
b. The average concentrations and percent reductions, as applicable, specified in subdivisions 2 b (1) through 2 b (4) of this subsection shall be computed and recorded, and shall be available for submittal to the board or review on-site by an inspector.
(1) All 24-hour daily geometric average sulfur dioxide emission concentrations and all 24-hour daily geometric average percent reductions in sulfur dioxide emissions as specified under 9VAC5-40-8140 D.
(2) All 24-hour daily arithmetic average nitrogen oxides emission concentrations as specified under 9VAC5-40-8140 G.
(3) All four-hour block or 24-hour daily arithmetic average carbon monoxide emission concentrations, as applicable, as specified under 9VAC5-40-8150 C.
(4) All four-hour block arithmetic average municipal waste combustor unit load levels and particulate matter control device inlet temperatures as specified under 9VAC5-40-8150 C.
3. Identification of the calendar dates when any of the average emission concentrations, percent reductions, or operating parameters recorded under subdivisions 2 b (1) through 2 b (4) of this subsection, or the opacity levels recorded under subdivision 2 a (1) of this subsection are above the applicable limits, with reasons for such exceedances and a description of corrective actions taken.
4. For affected facilities that apply activated carbon for mercury or dioxin/furan control, the records specified in subdivisions 4 a through 4 e of this subsection.
a. The average carbon mass feed rate (in kilograms per hour or pounds per hour) estimated as required under 9VAC5-40-8140 J 1 a during all annual emission tests for mercury emissions, with supporting calculations.
b. The average carbon mass feed rate (in kilograms per hour or pounds per hour) estimated as required under 9VAC5-40-8140 J 1 b during all annual emission tests for dioxin/furan, with supporting calculations.
c. The average carbon mass feed rate (in kilograms per hour or pounds per hour) estimated for each hour of operation as required under 9VAC5-40-8140 J 3 b, with supporting calculations.
d. The total carbon usage for each calendar quarter estimated as specified by 9VAC5-40-8140 J 3, with supporting calculations.
e. Carbon injection system operating parameter data for the parameter(s) that are the primary indicator(s) of carbon feed rate (e.g., screw feeder speed).
5. Identification of the calendar dates for which the minimum number of hours of any of the data specified in subdivisions 5 a through 5 e of this subsection have not been obtained including reasons for not obtaining sufficient data and a description of corrective actions taken.
a. Sulfur dioxide emissions data;
b. Nitrogen oxides emissions data;
c. Carbon monoxide emissions data;
d. Municipal waste combustor unit load data; and
e. Particulate matter control device temperature data.
6. Identification of each occurrence that sulfur dioxide emissions data, nitrogen oxides emissions data, or operational data (i.e., carbon monoxide emissions, unit load, and particulate matter control device temperature) have been excluded from the calculation of average emission concentrations or parameters, and the reasons for excluding the data.
7. The results of daily drift tests and quarterly accuracy determinations for sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides (large municipal waste combustors only), and carbon monoxide continuous emission monitoring systems, as required under Appendix F of 40 CFR Part 60, procedure 1.
8. The test reports documenting the results of all annual emission tests listed in subdivisions 8 a and 8 b of this subsection shall be recorded along with supporting calculations.
a. The results of all annual emission tests conducted to determine compliance with the particulate matter, opacity, cadmium, lead, mercury, dioxins/furans, hydrogen chloride, and fugitive ash emission limits.
b. For all dioxin/furan emission tests recorded under subdivision 8 a of this subsection, the maximum demonstrated municipal waste combustor unit load and maximum demonstrated particulate matter control device temperature (for each particulate matter control device).
9. The records specified in subdivisions 9 a through 9 c of this subsection.
a. Records showing the names of the municipal waste combustor chief facility operator, shift supervisors, and control room operators who have been provisionally certified by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers or an equivalent board-approved certification program as required by 9VAC5-40-8130 A, including the dates of initial and renewal certifications and documentation of current certification.
b. Records showing the names of the municipal waste combustor chief facility operator, shift supervisors, and control room operators who have been fully certified by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers or an equivalent board-approved certification program as required by 9VAC5-40-8130 B, including the dates of initial and renewal certifications and documentation of current certification.
c. Records showing the names of the municipal waste combustor chief facility operator, shift supervisors, and control room operators who have completed the EPA municipal waste combustor operator training course or a board-approved equivalent course as required by 9VAC5-40-8130 E, including documentation of training completion.
10. Records showing the names of persons who have completed a review of the operating manual as required by 9VAC5-40-8130 G, including the date of the initial review and subsequent annual reviews.
11. For affected facilities that apply activated carbon for mercury or dioxin/furan control, identification of the calendar dates when the average carbon mass feed rates recorded under subdivision 4 c of this subsection were less than either of the hourly carbon feed rates estimated during emission tests for mercury or dioxin/furan emissions and recorded under subdivisions 4 a and 4 b of this subsection, respectively, with reasons for such feed rates and a description of corrective actions taken.
12. For affected facilities that apply activated carbon for mercury or dioxin/furan control, identification of the calendar dates when the carbon injection system operating parameter(s) that are the primary indicator(s) of carbon mass feed rate (e.g., screw feeder speed) recorded under subdivision 4 d of this subsection are below the level(s) estimated during the emission tests as specified in 9VAC5-40-8140 J 1 a and 9VAC5-40-8140 J 1 b, with reasons for such occurrences and a description of corrective actions taken.
C. The owner of an air curtain incinerator subject to the opacity limit under 9VAC5-40-8060 shall maintain records of results of the opacity emission tests required by 9VAC5-40-8140 I for a period of at least five years.
D. The owner of an affected facility shall submit an annual report including the information specified in this subsection, as applicable, no later than February 1 of each year following the calendar year in which the data were collected (once the unit is subject to permitting requirements in a federal operating permit, the owner of an affected facility must submit these reports semiannually).
1. A summary of data collected for all pollutants and parameters regulated under this article, which includes the information specified in subdivisions 1 a through 1 e of this subsection.
a. A list of the particulate matter, opacity, cadmium, lead, mercury, dioxins/furans, hydrogen chloride, and fugitive ash emission levels achieved during the emission tests recorded under subdivision B 8 of this section.
b. A list of the highest emission level recorded for sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, municipal waste combustor unit load level, and particulate matter control device inlet temperature based on the data recorded under subdivisions B 2 b (1) through B 2 b (4) of this section.
c. List the highest opacity level measured, based on the data recorded under subdivision B 2 a (1) of this section.
d. The total number of days that the minimum number of hours of data for sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, municipal waste combustor unit load, and particulate matter control device temperature data were not obtained based on the data recorded under subdivision B 5 of this section.
e. The total number of hours that data for sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, municipal waste combustor unit load, and particulate matter control device temperature were excluded from the calculation of average emission concentrations or parameters based on the data recorded under subdivision B 6 of this section.
2. The summary of data reported under subdivision 1 of this subsection shall also provide the types of data specified in subdivision 1 of this subsection for the calendar year preceding the year being reported, in order to provide the board with a summary of the performance of the affected facility over a two-year period.
3. The summary of data including the information specified in subdivisions 1 and 2 of this subsection shall highlight any emission or parameter levels that did not achieve the emission or parameter limits specified under this article.
4. A notification of intent to begin the reduced dioxin/furan emission testing schedule specified in 9VAC5-40-8140 F 5 b during the following calendar year.
E. The owner of an affected facility shall submit a semiannual report that includes the information specified in subdivisions 1 through 5 of this subsection for any recorded pollutant or parameter that does not comply with the pollutant or parameter limit specified under this article, according to the schedule specified under subdivision 6 of this subsection.
1. The semiannual report shall include information recorded under subdivision B 3 of this section for sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, municipal waste combustor unit load level, particulate matter control device inlet temperature, and opacity.
2. For each date recorded as required by subdivision B 3 of this section and reported as required by subdivision 1 of this subsection, the semiannual report shall include the sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, municipal waste combustor unit load level, particulate matter control device inlet temperature, or opacity data, as applicable, recorded under subdivisions B 2 b (1) through B 2 b (4) and B 2 a (1) of this section, as applicable.
3. If the test reports recorded under subdivision B 8 of this section document any particulate matter, opacity, cadmium, lead, mercury, dioxins/furans, hydrogen chloride, and fugitive ash emission levels that were above the applicable pollutant limits, the semiannual report shall include a copy of the test report documenting the emission levels and the corrective actions taken.
4. The semiannual report shall include the information recorded under subdivision B 12 of this section for the carbon injection system operating parameter(s) that are the primary indicator(s) of carbon mass feed rate.
5. For each operating date reported as required by subdivision 4 of this subsection, the semiannual report shall include the carbon feed rate data recorded under subdivision B 4 c of this section.
6. Semiannual reports required by this subsection shall be submitted according to the schedule specified in subdivisions 6 a and 6 b of this subsection.
a. If the data reported in accordance with subdivisions 1 through 5 of this subsection were collected during the first calendar half, then the report shall be submitted by August 1 following the first calendar half.
b. If the data reported in accordance with subdivisions 1 through 5 of this subsection were collected during the second calendar half, then the report shall be submitted by February 1 following the second calendar half.
F. The owner of an air curtain incinerator subject to the opacity limit under 9VAC5-40-8060 shall submit the results of all annual emission tests for opacity recorded under subsection C of this section. Annual emission tests shall be submitted by February 1 of the year following the year of the emission test.
G. All reports specified under subsections D, E, and F of this section shall be submitted as a paper copy, postmarked on or before the submittal dates specified under these subsections, and maintained onsite as a paper copy for a period of five years.
H. All records specified under subsections B and C of this section shall be maintained onsite in either paper copy or computer-readable format, unless an alternative format is approved by the board.
I. If the owner of an affected facility would prefer to select a different annual or semiannual date for submitting the periodic reports required by subsections D, E, and F of this section, then the dates may be changed by mutual agreement between the owner and the board.
J. The owner of an affected facility shall submit the information specified in subdivisions 1 through 6 of this subsection in the initial emission test report.
1. The initial performance test data as recorded under subdivisions B 2 b (1) through (4) of this section for the initial emission test for sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, MWC combustor unit load level, and particulate matter control device inlet temperature.
2. The test report documenting the initial emission test recorded under subdivision B 8 of this section for particulate matter, opacity, cadmium, lead, mercury, dioxins/furans, hydrogen chloride, and fugitive ash emissions.
3. The performance evaluation of the continuous emission monitoring system using the applicable performance specifications in Appendix B of 40 CFR Part 60.
4. The maximum demonstrated MWC unit load and maximum demonstrated particulate matter control device inlet temperatures established during the initial dioxin/furan emission test as recorded in subdivision B 8 of this section.
5. For affected facilities that apply activated carbon injection for mercury control, the owner shall submit the average carbon mass feed rate recorded under subdivision B 4 a of this section.
6. For affected facilities that apply activated carbon injection for dioxin/furan control, the owner shall submit the average carbon mass feed rate recorded under subdivision B 4 b of this section.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999; amended, Virginia Register Volume 19, Issue 17, eff. July 1, 2003.
9VAC5-40-8170. Registration.
The provisions of 9VAC5-20-160 (Registration) apply.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999.
9VAC5-40-8180. Facility and control equipment maintenance or malfunction.
The provisions governing facility and control equipment maintenance or malfunction shall be as follows:
1. With regard to the emissions standards in 9VAC5-40-8080 and 9VAC5-40-8090, the provisions of 9VAC5-20-180 (Facility and control equipment maintenance or malfunction) apply.
2. With regard to the emission limits in 9VAC5-40-7970 through 9VAC5-40-8070, the following provisions apply:
a. 9VAC5-20-180 A, B, C, D, H, and I.
b. 9VAC5-40-8100 B.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999; amended, Virginia Register Volume 19, Issue 17, eff. July 1, 2003.
9VAC5-40-8190. Permits.
A permit may be required prior to beginning any of the activities specified below if the provisions of 9VAC5 Chapter 50 (9VAC5-50-10 et seq.) and 9VAC5 Chapter 80 (9VAC5-80-10 et seq.) apply. Owners contemplating such action should review those provisions and contact the appropriate regional office for guidance on whether those provisions apply.
1. Construction of a facility.
2. Reconstruction (replacement of more than half) of a facility.
3. Modification (any physical change to equipment) of a facility.
4. Relocation of a facility.
5. Reactivation (restart-up) of a facility.
6. Operation of a facility.
Statutory Authority
§ 10.1-1308 of the Code of Virginia.
Historical Notes
Derived from Virginia Register Volume 15, Issue 21, eff. August 4, 1999.